
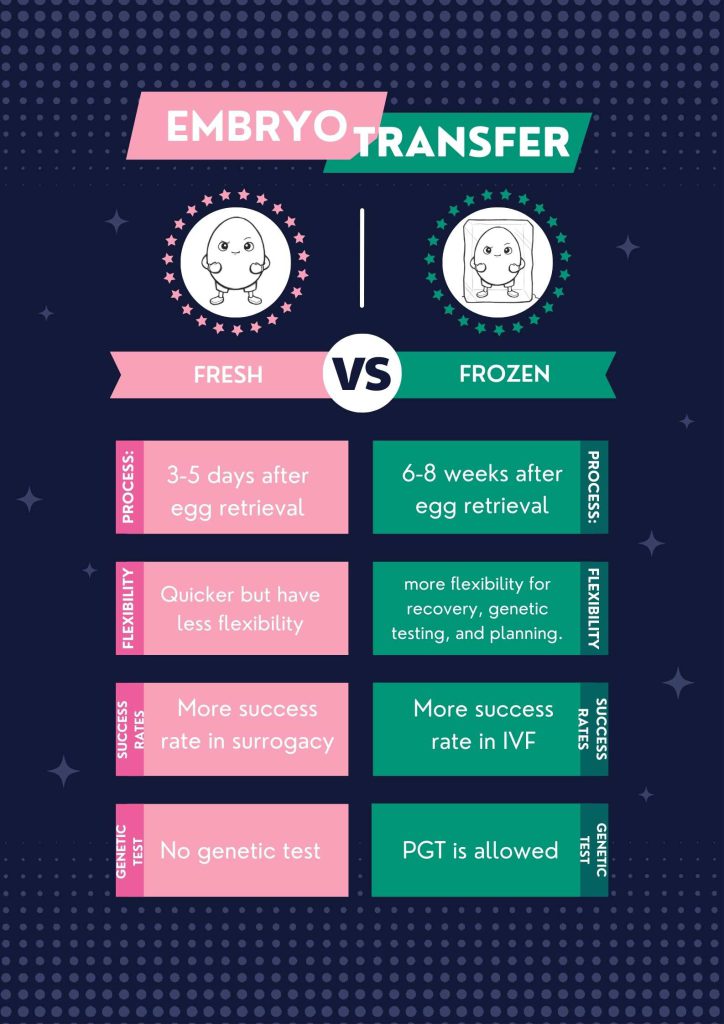
 Key Differences
- Timing: Fresh transfers occur in the same IVF cycle as egg retrieval, while frozen transfers are done in a subsequent cycle.
- Flexibility: Frozen transfers allow for recovery time and genetic testing, while fresh transfers are quicker but with less flexibility for testing and synchronization.
- Fresh Embryo Transfer: Success rates vary based on the woman’s age, ranging from 36.7% (under 35 years) to 9.3% (41 and older).
- Frozen Embryo Transfer: Generally higher success rates, ranging from 46.5% (under 35 years) to 25.9% (41 and older).
Both methods can have similar success rates, but frozen embryo transfer tends to have higher success rates across different age groups. Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) seems to offer more flexibility, better planning, and higher success rates compared to Fresh Embryo Transfer. However, the choice between the two methods may depend on individual circumstances, such as age and the specific needs and conditions of the patients.
You should know, if you want to go to foreign country for doing your IVF or surrogacy journey, FET is not recommended because you can’t go back to your home country, then come back to your destination for doing the ART procedure. In this case, we advise you to do fresh embryo transfer.
Our experimental evidences show us, for surrogacy, the success rate of fresh embryo transfer is too high and it should be done. However, for IVF and IVF related procedure there is no significant evidence to do fresh or frozen embryo transfer.
Key Differences
- Timing: Fresh transfers occur in the same IVF cycle as egg retrieval, while frozen transfers are done in a subsequent cycle.
- Flexibility: Frozen transfers allow for recovery time and genetic testing, while fresh transfers are quicker but with less flexibility for testing and synchronization.
- Fresh Embryo Transfer: Success rates vary based on the woman’s age, ranging from 36.7% (under 35 years) to 9.3% (41 and older).
- Frozen Embryo Transfer: Generally higher success rates, ranging from 46.5% (under 35 years) to 25.9% (41 and older).
Both methods can have similar success rates, but frozen embryo transfer tends to have higher success rates across different age groups. Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) seems to offer more flexibility, better planning, and higher success rates compared to Fresh Embryo Transfer. However, the choice between the two methods may depend on individual circumstances, such as age and the specific needs and conditions of the patients.
You should know, if you want to go to foreign country for doing your IVF or surrogacy journey, FET is not recommended because you can’t go back to your home country, then come back to your destination for doing the ART procedure. In this case, we advise you to do fresh embryo transfer.
Our experimental evidences show us, for surrogacy, the success rate of fresh embryo transfer is too high and it should be done. However, for IVF and IVF related procedure there is no significant evidence to do fresh or frozen embryo transfer.

Comments & Questions