Gastric Bypass Surgery or bariatric weight loss surgery
Obesity is a major health problem worldwide and has reached an epidemic proportion in the western and eastern society. Evidence continues to accumulate that obesity is a major risk factor for many diseases and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality.

A prospective, controlled Swedish study involving 4047 obese patients, half of whom had undergone bariatric procedures, followed up over 14.7 years, found that compared to usual care, bariatric surgery was associated with a significantly reduced number of cardiovascular deaths and a lower incidence of cardiovascular events in obese adults.
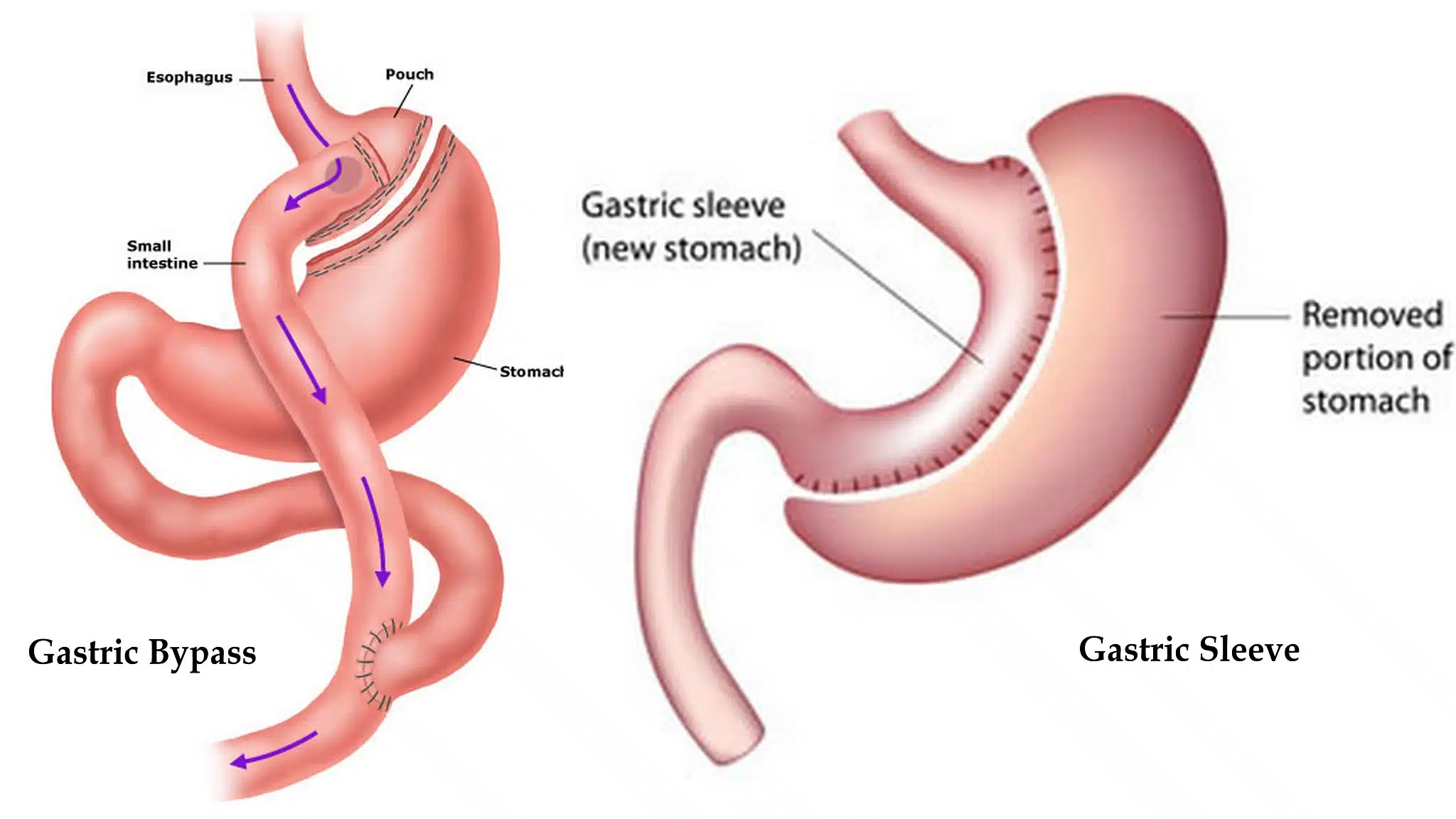
Modifications in the original procedures and the development of new techniques led to the following three basic concepts for bariatric surgery:
- Gastric restriction (adjustable gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy)
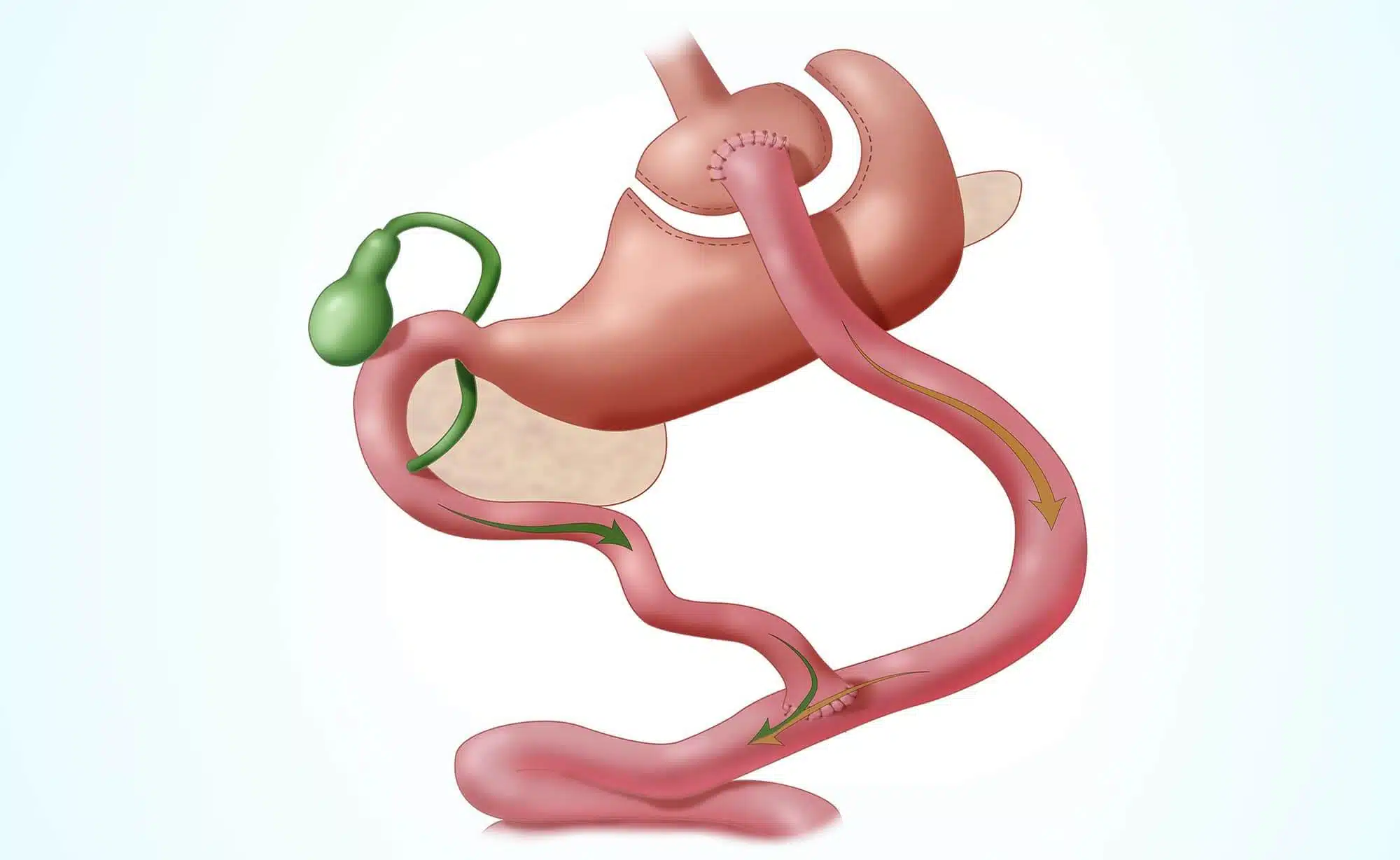
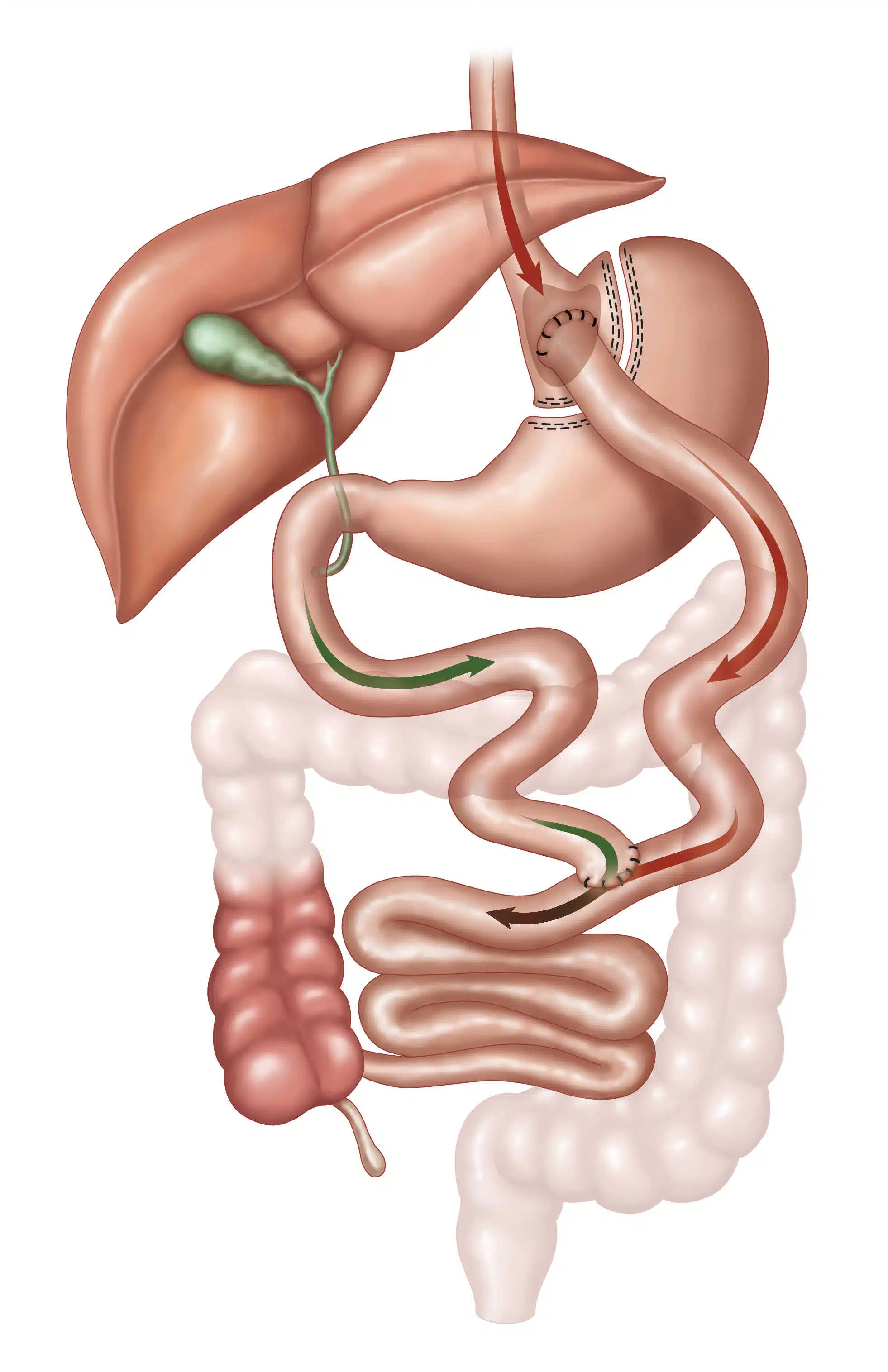
- Gastric restriction with mild malabsorption (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass)
- Combination of mild gastric restriction and malabsorption (duodenal switch)
Bariatric weight loss surgery cost in Iran by TebMedTourism company

Etiology
Obesity is a complex, multifactorial chronic disease influenced by the interaction of several factors, such as genetic, endocrine, metabolic, environmental (social and cultural), behavioral, and psychological components. The basic mechanism involves energy intake that exceeds energy output.
Epidemiology
The number of overweight individuals in the world is estimated at 1.7 billion. In the United States, the problem is at epidemic proportions. As much as two-thirds of the population in the United States are overweight, and half of the people in this group can be classified as obese. Gastric Bypass Surgery
History and Physical Examination
Morbid obesity is the harbinger of many other diseases that affect essentially every organ system, including the following:
- Cardiovascular (e.g., hypertension, atherosclerotic heart and peripheral vascular disease with myocardial infarction and cerebral vascular accidents, peripheral venous insufficiency, thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism)
- Respiratory (e.g., asthma, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity-hypoventilation syndrome)
- Metabolic (e.g., type 2 diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, hyperlipidemia)
- Musculoskeletal (e.g., back strain; disc disease; weight-bearing osteoarthritis of the hips, knees, ankles, and feet)
- Gastrointestinal (e.g., cholelithiasis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [steatosis steatohepatitis], hepatic cirrhosis, hepatic carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma)
- Urologic (e.g., stress incontinence)
- Endocrine and reproductive (e.g., polycystic ovary syndrome, increased the risk of pregnancy and fetal abnormalities, male hypogonadism)
- Cancer of the endometrium, breast, ovary, prostate, and pancreas
- Dermatologic (eg, intertriginous dermatitis)
- Neurologic (eg, pseudotumor cerebri, carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Psychologic (eg, depression, eating disorders, body image disturbance)
Approach Considerations
Surgery for obesity should be considered as a treatment of last resort after dieting, exercise, psychotherapy, and drug treatments have failed.
Favorable outcomes of bariatric surgery can lead to socioeconomic advancement, which may require patient guidance. Postoperative care may also include planning for reconstructive operations after weight stabilization for certain patients. Surgical options: Types of bariatric surgery include the following:
- Restrictive procedures (eg, adjustable gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy)
- Restrictive procedures with some malabsorption (eg, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass)
- Malabsorptive procedures with some restriction (eg, biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch)
Bariatric surgery can be performed either via an open approach or via a laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Surgery
Bariatric weight loss surgery in Iran:
Surgery time: On average from one and a half to two hours. Hospital stays: Normally three days. Recovery time: About two weeks. Since the surgery is done laparoscopically, recovery time is much shorter.
Depending on your job, you will be able to return to work in as soon as one or two weeks (desk job) or two to four weeks (if your job requires certain physical activities).
You will have a restriction of not lifting more than 10 pounds for a month and a half after the surgery. We know how hard the fight with obesity is. Members of our team have had the surgery themselves, and therefore our multidisciplinary team can talk from real-life experience about weight loss surgery and ‘the journey’ in detail about what to ‘really’ expect after surgery in Iran.