Surrogacy in Islam is a complex and often controversial topic, and it raises a range of ethical, legal, and religious questions. In the Islamic religion, surrogacy is a particularly sensitive issue, as it raises concerns about lineage, parentage, and the broader implications for the family and society.
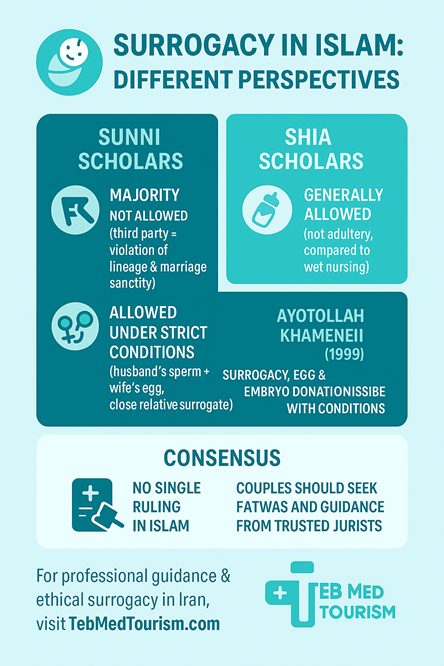
While there is no single Islamic perspective on surrogacy, there are various opinions among Islamic scholars regarding its permissibility and the circumstances under which it may be considered acceptable. Surrogacy in Islam can be discussed from two different points of view: Sunni and Shia schools of thought.
In order to examine the rulings of this process, candidates should refer to valid “fatwas” on surrogacy and the opinions of jurists. In this article, we will explore the Islamic perspective on surrogacy, including its religious and ethical aspects and the different opinions and interpretations of Islamic scholars on this topic.
Comparisons are also drawn with surrogacy in Christianity, where theological and moral debates often mirror those within Islam.
Is Surrogacy Allowed in Islam?
The issue of surrogacy in Islam is a topic of debate, and there are differing opinions on it among Islamic scholars and leaders, in both Sunni and Shia. It is important to note that there is no single authority in Islam that can make a definitive ruling on the permissibility of surrogacy.
As a result, Islamic leaders and scholars have different opinions on the matter. In Sunni Islam, the majority of scholars hold the view that surrogacy is not allowed, as it involves using a third party to conceive a child, which is seen as a violation of the natural order of procreation. Additionally, it may lead to issues of lineage and inheritance.
However, there are some Sunni scholars who consider surrogacy permissible under certain conditions, such as if the surrogate mother is a close relative or if the husband’s sperm is used.
In Shia Islam, there is generally a positive view on surrogacy. According to some of the major Shia scholars, surrogacy is permissible because it does not include a sinful act, and it is for the purpose of maintaining the family foundation.
There is no clear consensus among Islamic scholars on the acceptability of surrogacy in Islam, and opinions may vary depending on the specific circumstances and details of each case.
In general, many Islamic leaders and scholars consider surrogacy to be halal, or permissible, if it is done within the boundaries of Islamic family law and with the intention of fulfilling the desire for children while protecting the rights and well-being of all parties involved.
This debate has similarities with surrogacy from an ethical perspective, where discussions revolve around preserving family bonds, protecting children’s rights, and balancing religious traditions with medical advancements.
Surrogacy in Islam: Sunni Perspective
In Sunni jurisprudence, scholars are divided on the permissibility of surrogacy. Some accept it as a way to extend families, while others have a more negative stance towards IVF and surrogacy.
Critics argue that obtaining an egg or sperm from a third party is akin to sharing the marriage bed with someone else, which they compare to adultery. This is because the surrogate is carrying the fertilized egg of someone who is not her legal husband, rendering the act illegitimate.
Furthermore, they believe that since the biological mother has a genetic role in creating the baby, this could lead to emotional and legal conflicts between the two “mothers.”
Despite these concerns, Sunni scholars generally agree that the following conditions make fertility treatments permissible, provided the couple is still married:
- IVF with Embryo Transfer: Fertilization occurs outside the body by combining the husband’s sperm and the wife’s egg, and the embryo is then implanted into the wife’s uterus.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): The husband’s sperm is mechanically transferred into the wife’s uterus, allowing natural fertilization within her body.
These conditions ensure that no surrogate mother is involved. Both husband and wife must consent to the procedure, and it is recommended that the physician performing the treatment be a Muslim woman, if possible.
Surrogacy in the Hanafi and Shafi’i schools is considered acceptable as long as modern reproductive techniques use only the husband’s sperm and the wife’s egg. Additionally, some religious authorities permit surrogacy between co-wives under specific circumstances.
In conclusion, the diverse opinions in Sunni jurisprudence make it essential for couples to consult trusted jurists before proceeding.
Surrogacy can be a valuable method for strengthening family relationships through the blessing of children, but it must adhere to Islamic principles.
Surrogacy in Islam: Hanafi Perspective
In the Hanafi school of Islamic jurisprudence, surrogacy is generally permissible under specific conditions. Hanafi scholars support the use of surrogacy to help infertile couples conceive, provided that the arrangement adheres to Islamic law and ethical guidelines.
Conditions include ensuring clear lineage and discouraging commercialization. These views echo broader discussions on international surrogacy arrangements, where transparency and safeguarding family rights remain central concerns across cultures and religions.
While there may be some variation in opinion among Hanafi scholars, the general consensus is that surrogacy is permissible in certain circumstances, as long as it maintains clear ethical boundaries and adheres to Islamic law.
In summary, the Hanafi school acknowledges the role of modern reproductive techniques in addressing infertility, provided that the process respects Islamic values and safeguards the sanctity of marriage and family lineage.
Surrogacy in Islam: Shia Perspective
In 1999, Ayatollah Khamenei, the Supreme Jurisprudent of the Shia in Iran, ruled that under certain conditions surrogacy, egg, or embryo donations are all allowed.
“Transfer of the fetus to the uterus of the woman is not forbidden in any case, but touching and looking at the haram should be avoided,” he declared.
This position highlights why infertility treatment in Iran is highly advanced and widely trusted in the Muslim world. Iran’s legal and religious framework makes it one of the few Islamic countries where surrogacy is both permitted and practiced at a professional level.
His justification for allowing embryo donation is that the embryo is created from a married couple and is given to another married couple, and it does not involve direct sexual contact, so it cannot be called adultery.
This remarkable difference in Shia and Sunni attitudes about surrogacy originates from a different conception of the adultery act. In the Shia conception, adultery is physical and sexual bodily contact, not just transferring some cells.
Also, from the Shia point of view, adultery destroys the family, while donation (or surrogacy) protects it.
Surrogacy is acceptable based upon the objectives of Sharia, which are to protect one’s dignity and honor and also defend the preservation of the human species, which is one of the primary goals of Sharia.
The supporters of surrogacy in Islam consider it permissible by comparing it to ‘wet-nursing.’
Just like a foster mother who breastfeeds and gives nutrition to the baby, in surrogacy the baby is nourished by the surrogate mother. Therefore, they consider surrogacy and wet-nursing similar.
Is Surrogacy Haram in Islam?
As it was discussed above, the Islamic attitude toward involving a third party for reproduction is not united. Surrogacy from the point of view of a group of Sunni scholars is not an acceptable form of having children because they compare carrying the baby of a man who is not the mother’s legal husband to adultery, and they do not approve of this method.
However, other Sunni scholars and almost all religious leaders in Shia approve surrogacy. They believe that surrogacy should not be compared to adultery since it is not a sexual act. They compare surrogacy to wet nursing, where another woman only nourishes the baby, and she was not involved with embryo formation.
Overall, the debates on the issue of surrogacy are extensively done by the Islamic foghaha since each can have their own reasons to judge the morality of this process. Nevertheless, we cannot ignore the fact that surrogacy is one of the best ways to help infertile couples have children and grow their families.
What Does the Quran Say about Surrogacy?
The Quran, the central religious text of Islam, was revealed in the 7th century, long before the development of modern medical procedures such as surrogacy. Therefore, it does not directly address the concept of surrogacy.
However, it does provide principles and teachings related to parenthood, lineage, and the sanctity of marriage, which form the basis for Islamic jurisprudence when deliberating on modern issues such as surrogacy. One key principle in Islam is the preservation of lineage, with the Quran clearly defining relationships within a family and their rights.
Also, the Quran places a high value on the institution of marriage, and surrogacy, which traditionally involves a third party, can be seen to challenge this institution. This has led some scholars to have a more conservative view towards surrogacy. On the other hand, some scholars, looking at the broader Islamic principle of bringing relief and making things easier for believers, argue for a more compatible approach considering the use of surrogacy. This ongoing interpretation of Quranic principles in the context of surrogacy is reflective of the dynamic nature of Islamic jurisprudence as it responds to contemporary issues.
Is Surrogate Baby Halal or Haram?
The question of whether a surrogate baby is halal (permissible) or haram (forbidden) in Islam is a controversial subject, involving various aspects of faith, morality, and the dynamics of modern society. In Islam, family ties, marriage, and the bond between a mother and her child are important.
These values are crucial when discussing surrogacy. Whether surrogacy is permissible in religion depends on how these values are interpreted and applied to the situation. Islamic scholars and experts have different opinions on this issue. Some believe that surrogacy is acceptable as long as it does not violate the sanctity of marriage and maintains clear lineage.
Others believe that surrogacy is not allowed, as it goes against the natural way of creating a child and can cause confusion about lineage. It is important to consider these different views based on one’s own understanding, situation, and faith. There needs to be more discussion and understanding of this topic in the Muslim community to provide clearer and more inclusive guidance for those considering surrogacy.
What are the conditions for practicing surrogacy in Islam?
While the Quran does not directly address surrogacy, many Islamic scholars and jurists have sought to provide guidance on the conditions under which it may be permissible in Islam, based on interpretations of Islamic principles.
The consensus varies; however, some common themes have emerged in the discourse around this issue. A primary condition often cited is the preservation of marital sanctity and lineage. Some scholars suggest that surrogacy may be permissible if the egg and sperm are from the legally wedded couple and the surrogate is merely acting as a carrier, thus ensuring clear lineage.
Importantly, the intent behind the surrogacy process, the consent of all parties involved, and respect for the dignity of the surrogate are also considered paramount. This perspective underscores the importance of ethical conduct and noble intentions, key tenets of Islamic teachings.
Can Muslims be Surrogates?
Since the Islamic scholars have a different view on the subject of surrogacy, to fully answer the question “Can Muslims be surrogates?”, Encouraging open dialogue, scholarly discourse, and thorough education on surrogacy and its use within the Islamic community is vital.
Such constructive dialogues can lead to a deeper understanding and clearer guidelines for Muslims considering surrogacy. The topic of surrogacy in Islam is complex, influenced by a multitude of factors, including religious beliefs, societal norms, and personal circumstances.
The question of whether Muslims can be surrogates doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all answer but is an evolving dialogue in the intersection of faith, ethics, and modern medicine.
Is Surrogacy Haram in Islam Shia?
Surrogacy is a complex issue in Islam, but the majority of Shia scholars consider surrogacy permissible. Ayatollah Khamenei, Ayatollah Sistani, Ayatollah Golpayegani, and Ayatollah Makarem Shirazi have issued fatwas (religious rulings) allowing surrogacy under certain conditions.
Ayatollah Khamenei, the Supreme Leader of Iran, has stated that surrogacy is permissible if it is done with the couple’s own gametes (sperm and eggs) and with the intention of preserving the family and lineage. He has also emphasized the importance of transparency and honesty in the process and that the surrogate mother should have the right to know the identity of the biological parents.
Similarly, Ayatollah Sistani has allowed surrogacy if it is done with the couple’s own gametes and with the intention of preserving the family and lineage. He has also stressed that the surrogate mother should be treated with kindness and respect and that the child born through surrogacy should be considered the biological child of the couple and be given all the rights of a biological child.
It is recommended for those considering surrogacy to consult with a qualified religious authority and a medical professional to ensure that the process is done correctly and ethically.
Changes in Surrogacy in Islam in 2026
Surrogacy in Islam has always been a topic of significant debate, raising questions among many Muslims about whether it aligns with their religious beliefs and values. As modern healthcare advances, many wonder if surrogacy could eventually become a viable option for Muslim families across the globe.
As Islamic societies modernize, questions are being raised about whether surrogacy in Islam will become more widely accepted. While some countries still maintain prohibitions, making them part of the list of surrogacy laws, others are opening up to new reproductive technologies.
In recent years, countries like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have been changing in ways we couldn’t have imagined before. Things that were once considered taboo, like concerts by famous American and European singers, glamorous fashion shows, and large festivals, are now happening regularly.
These changes show that these countries are opening up socially and culturally, moving toward a more modern lifestyle. But could these changes also lead to new ideas in healthcare policies, especially in sensitive areas like fertility treatments and surrogacy in Islam?
Even if such changes are made in Islamic countries, it’s most likely that they will apply only to non-Muslims. For instance, in the UAE, one of the fertility treatments was recently legalized but specifically restricted to non-Muslims, highlighting how cultural and religious considerations continue to shape healthcare policies in the region.
Iran, on the other hand, has been a leader in fertility treatments for many years. Surrogacy in Iran is supported by Islamic rulings and practiced professionally and ethically. Unlike some countries that restrict such services, Iran has been offering fertility treatments, including surrogacy, to both Muslims and non-Muslims for many years. This inclusivity has made Iran a trusted destination for families from diverse backgrounds.
At TebMedTourism, we’ve been helping couples from around the world with services like surrogacy, IVF, egg and sperm donation, and gender selection. Our team includes some of the best fertility specialists in the world, and our success rates are among the highest. Most importantly, our services are offered at very affordable prices compared to other countries, making it possible for families to achieve their dream of parenthood without unnecessary financial stress.
If these changes happen in the Middle East, it will still take years for new systems to reach the level of professionalism and success that Iran has achieved. For couples considering surrogacy or other fertility treatments, Iran remains a top destination, and TebMedTourism is here to guide you through every step of the journey.
If you’d like to learn more about the process, don’t forget to check out our article: Surrogacy in Iran.
Conclusion
To sum up, surrogacy in Islam is a multifaceted issue involving law, ethics, and religion. While certain countries forbid it—thus falling into the illegal surrogacy countries—others, like Iran, allow it under strict conditions. For families looking into safe and ethical fertility solutions, infertility treatment in Iran remains one of the most reputable choices.
Surrogacy in Iran is not only legally supported but also religiously approved. TebMedTourism, as one of the most experienced surrogacy companies, organizes all the medical and legal requirements of this process for prospective parents so that they are able to focus on the arrival of their baby with peace of mind.
Our professional medical team at TebMedTourism Co. is ready to guide you and answer your further questions about surrogacy. We will lead you the way till the end of the journey. Contact TebMedTourism Co. now, free of charge, all through the week.
Is surrogacy permissible in Islam?
There is no single ruling. Most Sunni scholars forbid it, seeing it as involving a third party in procreation, but some allow it under strict conditions. Shia scholars, including Ayatollah Khamenei and others, generally permit it if done with the couple’s own gametes and within Islamic ethical boundaries.
Does surrogacy conflict with Islamic rules of mahram?
Yes, some scholars argue it may create lineage and mahram confusion. Others, especially in Shia thought, compare it to wet-nursing, where the surrogate nourishes but does not affect parentage, so mahram rules remain clear if lineage is well-documented.
Is receiving payment for surrogacy allowed in Islam?
Opinions differ. Many jurists discourage commercialization to protect dignity and lineage, though compensation for medical costs and efforts may be considered acceptable in some rulings.
Is surrogacy compatible with human dignity in Islam?
Supporters argue that it protects family life and helps preserve human lineage, aligning with Sharia goals. Critics say it risks treating women’s bodies as commodities and undermines the sanctity of marriage.
Is surrogacy common in Islamic countries?
It is restricted in most Sunni-majority countries, but Iran (a Shia-majority country) has advanced fertility programs where surrogacy is legally and religiously permitted, making it a leading destination for such treatments.