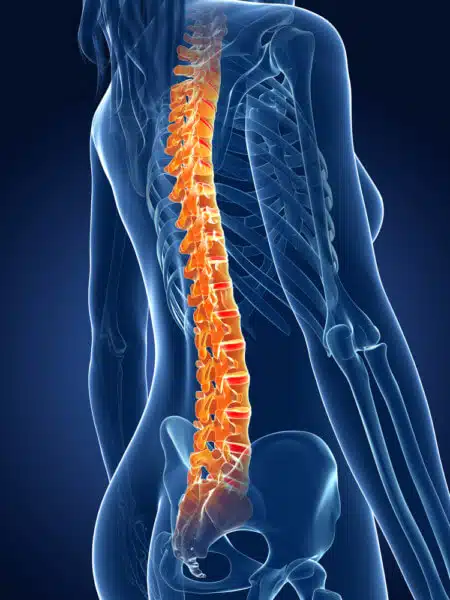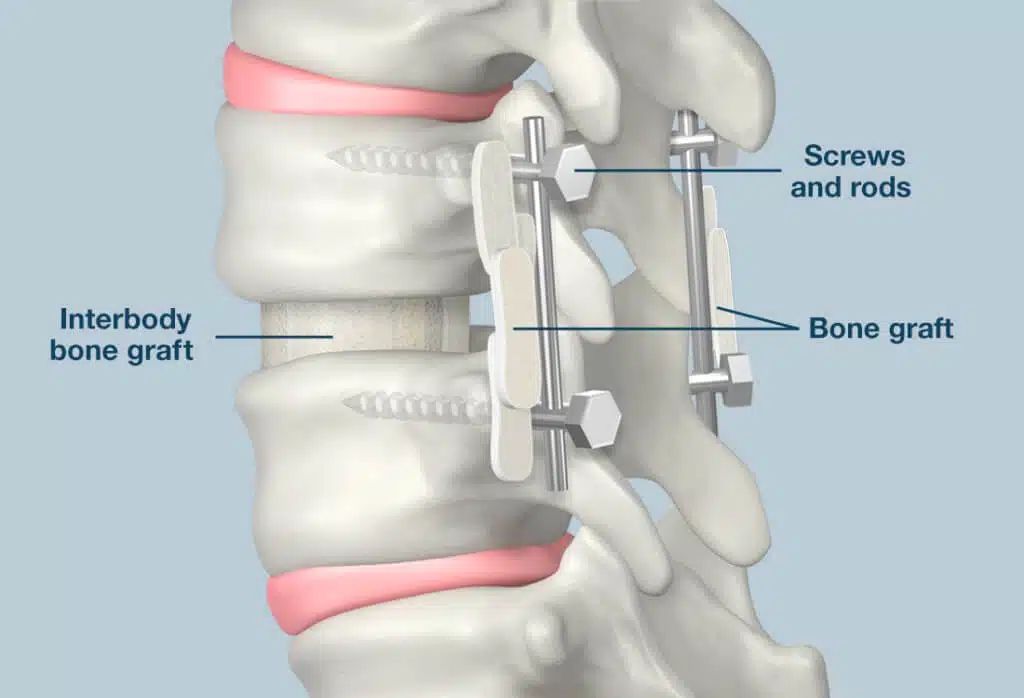
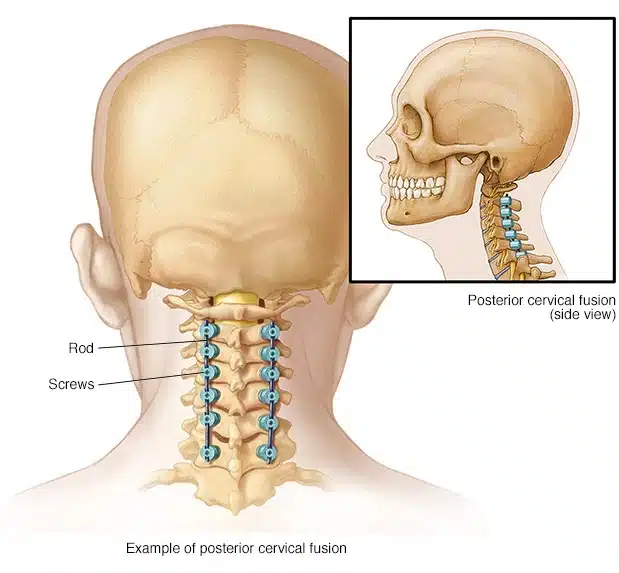
Posterior spinal fusion is a procedure where an extra bone or a bone-like material is fused in the space between spinal vertebrae and makes one solid bone. The surgery aims to improve your spine stability or correct its deformity to eliminate pain. It is named posterior as the incision is made at the back of the body.
What is Spinal fusion?
Posterior spinal fusion is a surgery to stabilize the spine. During the procedure two or more vertebrae are joined into one bone permanently and no space remains between them. Thus, extra bone is used to fill the space. It is done to relieve pressure on the patient’s irritated nerves and assure that it will not return. The pressure on the spinal nerve leads to leg or back pain, weakness, numbness or lack of coordination.
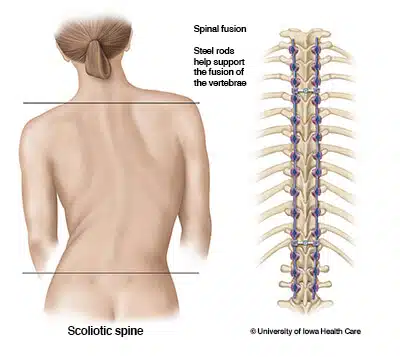
Spinal fusion surgery is recommended to treat:
- Deformities of the spine
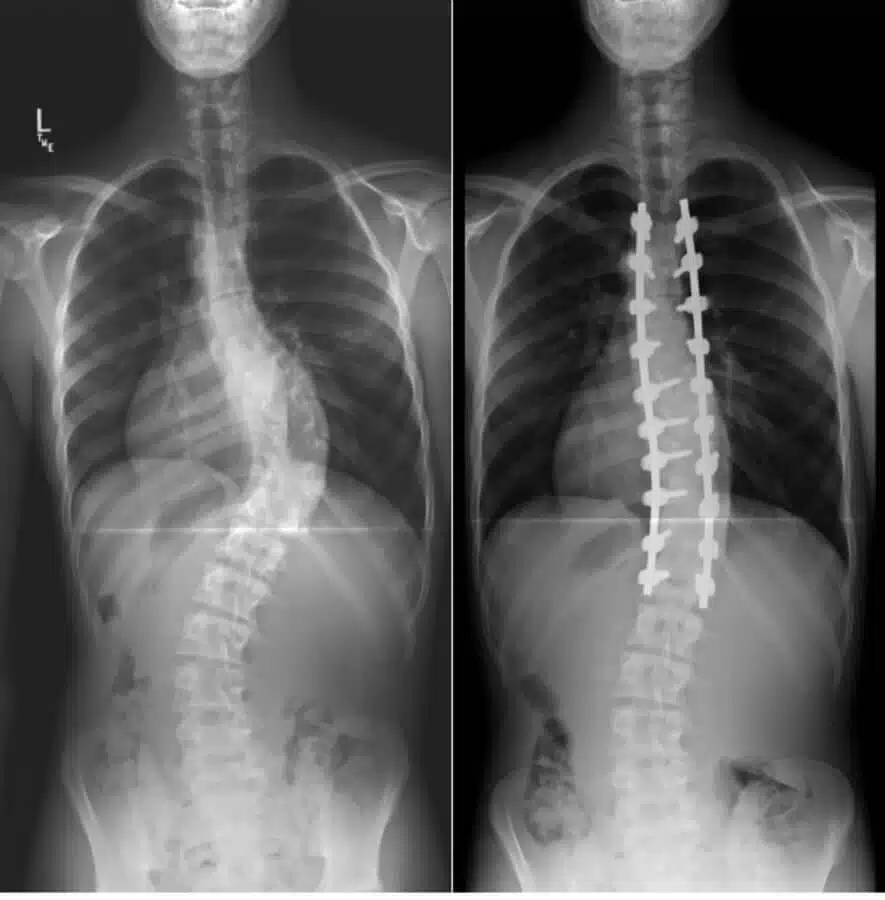
- Correct spinal deformities such as scoliosis (spine curve).
- Spinal weakness or instability
- Severe arthritis may lead to side effects such as the abnormal or excessive motion between your two vertebrae. Spinal fusion can restore spinal stability.
- Herniated disk: It will stabilize the spine after hernia removal from your disk.
The posterior spinal fusion success rate is high, but like any other surgery it may have some risks including:
- Spinal cord or nerve root injury
- Failure of fusion
- Dural tear
- Infection
- Other complications such as blood clots and pneumonia.
How posterior spinal fusion is different from anterior spinal fusion?
The anterior method is taken while you are lying in a spine position, and the incision is made in your abdomen or your throat. This approach includes:
- Anterior lumbar vertebra inter-body fusion
- Anterolateral method
- Retroperitoneal method
- Direct lateral inter-body fusion
- Extreme lateral inter-body fusion
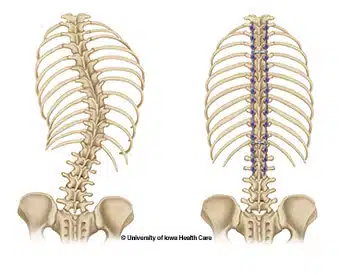
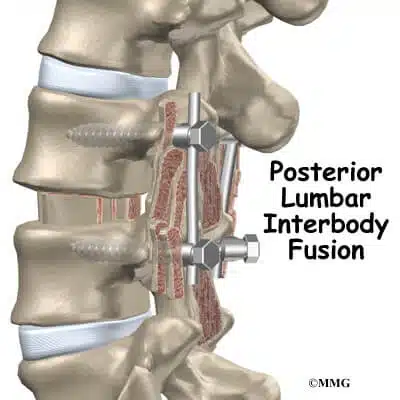
However, the posterior approach is done while you lie face down. The incision is made at the back of body. This approach is generally done when one or two of your spinal levels are being fused along with posterior instrumentation and decompression. This approach includes:
- Posterior interbody fusion
- Posterior lumbar interbody fusion
- Posterolateral technique
- Axial lumbar interbody fusion
- Transverse process technique
The procedure
This procedure is done under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision in your abdomen or your throat to be able to access your spine from the front. As previously mentioned, the surgeon uses the extra bone to fill the gap between vertebrates. Bone graft preparation is important to work. The surgeon can take it from a bone bank or it can come from your own body. The surgeon removes the disc material and facet joints. He/she may remove all facet joints or just part of them. Then he/she packs the space with bone graft. Then, the surgeon inserts screws, spacers and rods into the bones to hold everything in place temporarily.