PCOS diet is one of the most important strategies for controlling and treating this problem. Many women who suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) discover that following a suitable PCOS diet plan helps them control their symptoms, such as irregular periods, weight gain, acne, and difficulty conceiving.
A balanced PCOS diet plan frequently entails limiting refined carbs and sugary foods and increasing the consumption of lean protein and high-fiber foods.
If you’ve looked into diets for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), you may have come across recommendations that say eating one meal or avoiding another can “fix” everything.
In reality, there is no diet or food that may treat PCOS; however, your diet might affect how you feel. This guide also works as a PCOS diet for beginners, offering practical and sustainable recommendations.
What is PCOS?
PCOS, or polycystic ovary syndrome, is a common hormonal disorder that affects women who are fertile. Adolescence is when it typically begins, but symptoms might change over time and may be influenced by factors such as hormonal balance and Ovarian Reserve.
Hormonal abnormalities, irregular periods, high androgen levels, and ovarian cysts can all be symptoms of PCOS. It might be challenging to get pregnant if you have irregular periods, which is why PCOS is one of the major causes of infertility. Many individuals explore advanced options such as infertility treatment in Iran.
As a chronic illness, PCOS is incurable. However, certain symptoms can be alleviated by medicine, fertility therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Although the exact origin of PCOS is unknown, women who have type 2 diabetes or a familial history are more vulnerable.
How does diet affect PCOS?
Regulating the body’s insulin levels is one of the main tasks of the PCOS diet. Insulin levels that are greater than normal are frequently observed in PCOS patients. The hormone insulin is made by the pancreas. It facilitates the body’s cells’ conversion of sugar, or glucose, into energy.
Your blood sugar can increase if you don’t make enough insulin. This may also occur if you have insulin resistance, which is the inability to efficiently use the insulin that you do make.
Your body may try to produce a lot of insulin if you have insulin resistance in an attempt to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Your ovaries may create more testosterone and other androgens if your insulin levels are too high.
A greater body mass index might also contribute to insulin resistance. People with PCOS frequently struggle to lose weight because insulin resistance might make it more difficult.
A diet heavy in refined carbs, such as sweet and starchy foods, might make managing insulin resistance and, thus, weight reduction more challenging. This is why a PCOS insulin resistance diet focuses on stabilizing blood sugar levels through low-glycemic, whole foods.
Best foods to eat if you have PCOS
Research from 2019 by NIH indicates that between 33% and 83% of PCOS patients are also overweight or obese. Adopting a targeted PCOS weight loss diet and exercise routine can help reduce these risks and improve ovulation.
Individuals with PCOS may also be more vulnerable to the following, especially if their symptoms are not controlled:
- Endometrial cancer and Heart disease
- High blood pressure with diabetes
With dietary and lifestyle modifications, many women who have PCOS discover they can control their symptoms and lower their chance of developing other health issues.
Below, we will introduce the most important foods in the PCOS diet:
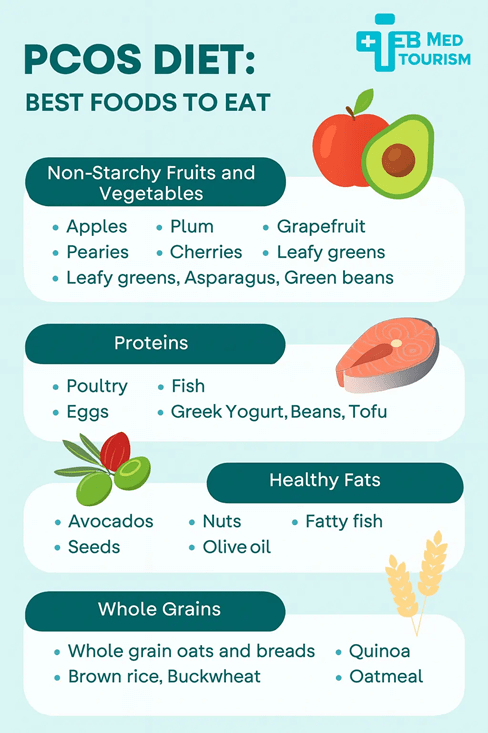
Non-starchy fruits and vegetables
The glycemic index of non-starchy fruits and vegetables is low. The glycemic index (GI) is a number between 1 and 100. The longer it takes for food to elevate a person’s blood sugar levels, the lower the score.
After being digested, glucose is gradually released into the bloodstream from foods having a low glycemic index. This may lessen the chance of abrupt increases in blood sugar. Fruits and vegetables having a low glycemic index include the following:
- Apples
- Pears
- Plums
- Grapefruit
- Cherries
- Leafy green vegetables
- Asparagus
- Green beans
Proteins
According to some studies, eating a diet higher in protein and lower in carbohydrates can help alleviate insulin resistance in people with PCOS. Think about eating:
- Poultry, such as chicken or turkey
- Fish, such as salmon, shrimp or cod
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Beans
- Tofu
Healthy fats
People have a negative perception of fats. However, not every dietary fat is created equal. Healthy fats are unsaturated fats. They can assist in balancing your hormones and reducing inflammation in your body.
Acne, irregular menstruation periods, and other issues are caused by hormone abnormalities in PCOS, particularly excessive levels of androgens. One approach to help balance that out is to eat a lot of healthy fats.
Add these healthy fats to your diet:
- Avocados
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Fatty fish
- Olive oil
Whole grains
Your body processes whole grains more slowly than it does simple, refined carbohydrates. They have a lower glycemic index and do not result in blood sugar or insulin rises. Here are a few instances of entire grains:
- Whole grain pastas and breads
- Quinoa
- Oatmeal
- Brown rice
- Buckwheat
Foods to avoid if you have PCOS
Refined carbohydrates should be avoided or severely restricted since they worsen insulin resistance and induce inflammation. The following items are highly processed foods and commonly included on a PCOS food list to avoid.
- White bread
- Muffins
- Breakfast pastries
- Sugary desserts
- Anything made with white flour
Pasta noodles with semolina, durum flour, or durum wheat flour listed as the primary ingredient are low in fiber and high in carbs. A healthy substitute for wheat flour is pasta prepared from bean or lentil flour.
A PCOS diet should restrict sugar because it is a carbohydrate. Make sure to look for the different names of sugar on food labels, such as
- Sucrose
- High fructose corn syrup
- Dextrose
On a PCOS diet, you might want to cut back on inflammatory foods like fries, margarine, and red or processed meats, as well as sugar-rich beverages like juice and soda.
However, it’s best to speak with a healthcare provider before cutting out specific foods from your diet. They might suggest a diet plan tailored to your specific requirements. Certain lifestyle modifications can alleviate PCOS symptoms.
Exercise and regular physical activity are part of these improvements. Both can lessen insulin resistance when combined with a restricted consumption of refined carbs. Exercise should consist of at least 150 minutes per week, according to many experts.
Weight loss may also result from regular exercise, a low-sugar diet, and a low-inflammation diet. When people lose weight, their ovulation may improve.
Trans and saturated fats
Inflammation and insulin resistance can be enhanced by diets heavy in trans and saturated fats. Aim to consume no more than 30% of your calories from fat, and steer clear of or restrict trans or saturated fats like:
- Red meats, particularly processed meats like those found in fast-food hamburgers
- Donuts, pies, and cookies are examples of baked goods.
- Pizza that is frozen
- Popcorn in the microwave
- Fried dishes, such as fried chicken and french fries
- Margarine
Simple carbohydrates
Eating a lot of processed meals and simple carbohydrates is the main cause of insulin resistance. These carbohydrates, which are composed of sugars like fructose and glucose, can raise blood sugar and insulin production quickly, which might result in health problems. Try to restrict or stay away from:
- Pizza dough
- Cakes and cookies
- Sweetened cereals
- White bread and pasta
- White rice
Beverages with added sugars
An excessive amount of sugar can lead to inflammation in the body, which can be detrimental to PCOS sufferers.
When it comes to examples of sugary drinks, drinking soda might seem apparent, but you might not be aware that your morning smoothie—especially if it comes from a shop bottle—can still contain enough sugar to cause a blood sugar increase.
Rather, continue to consume entire fruits rather than liquids. Beverages to limit include, for example:
- Soda
- Cold-pressed juice
- Bottled smoothies
- Fruit juices
- Cocktails made with sugary mixers
Certain dairy products
According to one study, milk consumption directly affects those who have PCOS. Reducing your dairy consumption may help lessen the symptoms of PCOS.
However, not everyone is impacted by dairy in the same way, so it’s definitely alright to keep eating it if you don’t have any worsening symptoms. You might want to stay away from the following dairy products:
- Sugar-sweetened regular yogurt
- Cheeses with a lot of processing
- Sugar-infused ice cream
- Whole milk
PCOS Diet Plan to Get Pregnant
For those trying to conceive, a PCOS diet plan to get pregnant focuses on improving insulin sensitivity, supporting ovulation, and reducing inflammation. Combining a balanced diet with regular exercise and weight management may improve fertility outcomes and can support medical options such as IVF in Iran or egg donation in Iran when advised by a specialist.
Other lifestyle changes to consider with PCOS
Certain lifestyle modifications can alleviate PCOS symptoms. In the following we will consider some lifestyle changes that are suitable when dealing with PCOS:
Exercise and regular physical activity are part of these improvements. Both can lessen insulin resistance when combined with a restricted consumption of refined carbs. Exercise should consist of at least 150 minutes per week, according to many experts.
Weight loss may also result from regular exercise, a low-sugar diet, and a low-inflammation diet. When people lose weight, their ovulation may improve.
Stress may be brought on by PCOS symptoms. Techniques for reducing stress that help you connect with your body and relax your thoughts can be beneficial. Yoga and meditation are two of these. Additionally, consulting a therapist or other medical expert could be helpful.
Conclusion
Making modifications to your lifestyle and eating a PCOS-friendly diet may help you feel better and lessen some of the symptoms that come with having PCOS.
Be aware that you may wish to restrict or stay away from certain foods when following a PCOS diet. But these foods often have healthy, nutrient-dense alternatives. For instance, if you often have white toast and margarine for morning, consider switching to high-fiber whole grain bread with avocado or olive oil.
What foods should I avoid with PCOS?
People with PCOS should stay away from refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and highly processed foods. Foods that may worsen insulin resistance and inflammation include white bread, pastries, sugary sweets, sweetened beverages, fried foods, processed meats, and foods high in trans and saturated fats.
What is the best diet to manage PCOS?
The best diet for managing PCOS is one that stabilizes blood sugar and improves insulin sensitivity. Examples of this include whole grains, lean meats, non-starchy fruits and vegetables, and healthy fats; avoid processed carbs, sweets, and inflammatory meals.
Can I eat eggs with PCOS?
Yes, eggs are a wonderful option for PCOS sufferers. When incorporated into a balanced diet, they are an excellent source of protein that can help maintain blood sugar balance and lessen insulin spikes.
How much protein does a polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) diet need?
Compared to regular diets, a PCOS diet usually benefits from a higher protein consumption. Protein-rich foods like fish, chicken, eggs, beans, tofu, or Greek yogurt can help reduce insulin resistance and promote weight control at every meal.
How many calories should someone with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) consume?
Age, degree of exercise, and health objectives all affect calorie requirements. Many PCOS patients experience weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and hormonal balance when they follow a low-calorie diet and engage in regular exercise. The ideal calorie range can be identified with the assistance of a medical professional.