Kidney transplant in Iran is one of the medical surgeries that has attracted the attention of many people around the world due to its very high quality and reasonable price. The kidneys are essential organs, and they clear the blood of toxins and create the urine that is used to move pollutants out of the body. The kidneys also control the body’s water balance. Kidney failure causes the body to poison itself, which quickly results in death.
As a result, a patient whose kidneys are no longer functional must either have a kidney transplant from a donor or undergo continuous dialysis treatment, which involves machine blood purification.
Kidney transplant in Iran is typically the desired outcome because dialysis must be performed multiple times a week for several hours, significantly restricting the patient’s daily life. Furthermore, a Kidney transplant success rate in Iran increases the patient’s life expectancy.
What is a Kidney Transplant?
A kidney transplant, also known as kidney replacement surgery in Iran, is an operation done to replace a damaged or injured kidney with a healthy kidney from a donor. A living donor or a deceased organ donor may provide the kidney.
One kidney may be donated by family members or those who are a good match. This form of transplant is called a live transplant. One healthy kidney can sustain a person’s life after kidney donation. This process may also involve living with one kidney donation, which most recipients adapt to without major complications.
A person having a transplant most commonly gets just one kidney. They might occasionally receive two kidneys from a deceased donor. The diseased kidneys are usually kept in place. The transplanted kidney is inserted in the lower belly on the front side of the body.
Who May Need a Kidney Transplant in Iran?
Although a kidney transplant has lots of advantages, it also has serious disadvantages that may make it too dangerous for some individuals.
Therefore, a kidney transplant is usually the best treatment for renal failure in patients who are fit enough for the operation; however, the benefits must outweigh the risks. Potential candidates for kidney transplantation include the following patients:
People with chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) damages the kidneys, which over time may not be able to clean the blood as well as healthy kidneys. When the kidneys fail to function properly, toxic waste and excess fluid build up in the body, which can cause high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, and early death.
People with acute kidney injury (AKI)
When the kidneys are suddenly unable to filter waste from the bloodstream, acute kidney damage occurs. Toxic waste levels may accumulate when the kidneys are unable to filter waste. The chemical composition of the blood may become unbalanced.
Acute renal damage used to be called acute kidney failure. Acute kidney injury is more common in persons who are in the hospital, mainly in people who need intensive care.
Acute renal damage ranges from moderate to severe. It can be fatal if severe, persistent, and untreated. But it also can be reversed. Individuals in otherwise healthy conditions may regain normal or almost normal kidney function.
People with congenital kidney problems
Many congenital kidney and urinary tract issues can lead to recurrent UTIs and scarring of the kidneys if they are not identified in time, further impairing kidney function. Over time, these disorders may progress to chronic renal disease and hypertension, which can impact a child’s growth and development.
What are the Methods for Obtaining a Kidney for Transplant Surgery in Iran?
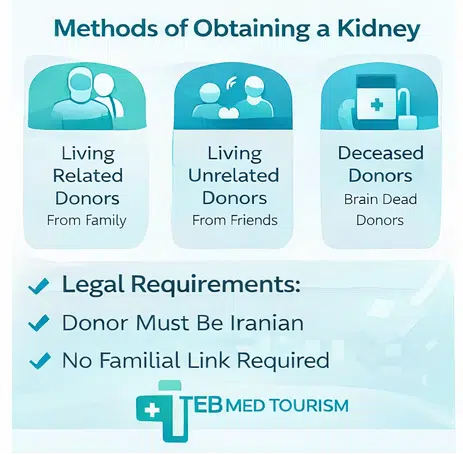
A kidney can be obtained in three primary ways, including the following:
- Living Related Donors: A living related donor is a kidney given by a close relative, such as a parent, sibling, or child. These donors often have a better chance of compatibility because of shared genetic traits.
- Living Unrelated Donors: Individuals who are not connected by blood can also donate their kidneys. This group includes friends or humanitarian donors who voluntarily help others in need.
- Organs from deceased donors: They can remove kidneys from individuals who have been deemed brain dead but whose organs are still donatable.
Brain tumors, strokes, and serious injuries are the most common causes of death for these donors. They are removed shortly after death in order for the organs to continue to function.
What are the Legal Requirements for Kidney Transplant in Iran?
According to Iranian law regarding kidney donation, Iranians are prohibited from donating their kidneys to non-Iranian recipients. Consequently, medical tourists seeking kidney transplantation in Iran must have a donor with the same nationality.
Iran doesn’t require that the donor and the recipient have a family relationship, in contrast to many other countries. Kidneys might be donated by friends, acquaintances, or even selfless individuals of the same nationality. The choice of appropriate donors is therefore more flexible.
How to Get Prepared for a Kidney Transplant in Iran?
The process of kidney transplant in Iran is meticulous and meticulously planned ensuring the best outcomes for patients. One important factor patients often ask about is kidney transplant surgery time in Iran, which varies depending on donor type and patient condition.
In Iran a comprehensive physical examination including blood tests and kidney-related assessments is required of both donors and recipients before they can receive a kidney transplant in Iran . Most of these tests even if you have already finished them in your home country need to be repeated in Iran.
Kidney transplant tests include urine tests and compatibility testing, including tissue typing, blood typing, and kidney crossmatching, to determine eligibility.
Necessary tests before kidney transplant in Iran (brief explanation)
To decide whether to put the patient on the transplant waiting list, a thorough health evaluation will be conducted. Urine tests and compatibility testing, including tissue typing, blood typing, and kidney crossmatching, are some of the tests before a kidney transplant.
In the following, we will explain some of the tests for obtaining medical eligibility before surgery:
Blood type testing
Your ABO blood type is determined by the first test. Everybody belongs to one of the four inherited blood types, which are A, B, AB, and O. Both the donor and the recipient must have compatible or identical blood types. Donor matching does not take the Rh type (+, -) into account.
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA)
Tissue typing is the second test, which is a blood test for human leukocyte antigens (HLA). Although these antigens are present on many bodily cells, they are primarily observed on white blood cells. The degree of tissue type similarity across family members can vary from 100% to 0%. Donor selection takes into account each possible donor’s tissue type.
The transplant team can make the necessary arrangements for the tissue-typing test with the potential recipient as well as any interested family members and non-relatives. Results are ready in two weeks, and no extra preparation is needed.
You can mail pre-packaged kits with detailed instructions on how to take and return blood samples to family who live out of town. A nearby doctor’s office or hospital laboratory can draw the required blood, which can then be returned to the transplant program.
Crossmatch
Your body produces chemicals known as antibodies throughout your life that work to eliminate foreign substances. Every time you get an infection, become pregnant, receive a blood transfusion, or receive a kidney transplant, you may produce antibodies. Your body will destroy the donor kidney if you have antibodies against it.
Because of this, we test you to make sure you don’t already have antibodies to the donor when a kidney is available for you. We refer to this test as a crossmatch. Your blood and donor cells are combined to perform the crossmatch. You should not receive this specific kidney if the crossmatch is positive because it indicates that you have antibodies against the donor.
Serology
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis, and cytomegalovirus (CMV) are among the potentially contagious disorders for which blood testing is performed.
UCSF Health medical professionals have looked over this data. Just to be clear it is not intended to replace the advice of your physician or any other healthcare professional. We recommend that you discuss any questions or concerns you may have with your provider.
How is a Kidney Transplant Process Done in Iran?
The process of kidney transplant in Iran is meticulous and meticulously planned ensuring the best outcomes for patients. Below is a summary of the typical procedures.
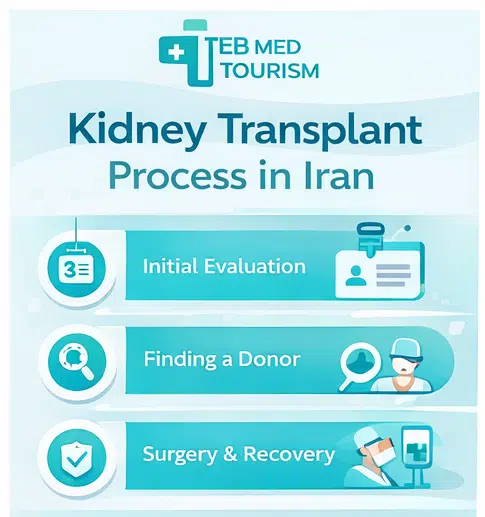
1. Initial Evaluation: Getting a kidney transplant begins with an evaluation. Your transplant team will need to know about your health support system and insurance through a series of appointments and tests. The evaluation helps the team decide whether a transplant is a safe treatment option for you.
2. Finding a Kidney Donor: In the kidney transplant process one of the most crucial steps is finding a suitable kidney donor. A living person (a friend family member or relative) or a deceased or brain-dead person can both be a donor. Since kidney transplant success rates are generally higher living donors are usually preferred due to their greater compatibility.
The patient’s blood type and the availability of suitable donors are two factors that may affect the time needed for a kidney transplant; patients who do not have a living donor may be placed on a waitlist for a deceased or brain-dead donor. Patients can get help controlling their wait times and if needed looking into options such as matched exchange which transfers donors to a patient who matches them.
3. Post-transplant care: In order to manage medication keep an eye on the transplants functionality and avoid complications patients must receive thorough post-transplant care after surgery. Following up with transplant specialists on a regular basis is essential to ensuring the transplants long-term success.
Post-operative care is one of the crucial phases of the kidney transplant procedure. During this time, the patient must follow a post kidney transplant diet plan under the supervision of a nutritionist.
To stop the body from rejecting the new organ patients also take kidney transplnant anti-rejection drugs . Understanding kidney rejection symptoms is essential for preserving transplant health and facilitating early intervention.
4. Support and Rehabilitation: Support services and rehabilitation programs are provided to assist patients in acclimating to life following transplantation. To enhance general wellbeing this could involve physical therapy nutritional counseling and emotional support.
What to Expect After Kidney Transplant in Iran?
After kidney transplantation in Iran, recipients are first kept under strict observation in a recovery room. When their vital signs including heart rate blood pressure and breathing stabilize and they become conscious again they are moved to the intensive care unit (ICU) for additional monitoring.
Tehrani kidney specialists keep a close eye on the patients health during this crucial time. Most patients spend a few days at Tehran Kidney Hospital. Monitoring vital signs controlling pain making sure the new kidney works correctly and taking care of any possible post-kidney transplant complications—like infections or bleeding—all depend on this period.
After transplantation the kidney usually starts to work and produce urine if it comes from a living donor. Nevertheless patients who receive a kidney from a deceased donor might need short-term dialysis care until the new kidney functions properly.
Urine is drained via a catheter and the kidneys condition is evaluated by routine blood tests. As recuperation advances the patients diet progressively shifts from IV fluids to typical meals. In addition to taking the anti-rejection medication they require for life patients will learn how to take care of themselves at home.
Patients are prepared to go back home once their vital signs have stabilized and their kidney transplant is operating normally. Monitoring kidney transplant recovery time is essential for a safe return to daily life.
Other considerations include pregnancy after kidney transplant for women and long-term adaptation, especially for those living with one kidney donation.
Possible infections after kidney transplant
Chest infections, as one of the kidney transplant facts, frequently occur during the initial week following a transplant (affecting 10 out of 100 patients). Typically, these infections are effectively treated with antibiotics over a course of 5-7 days. Quitting smoking while awaiting a transplant will lower the chances of developing a chest infection.
Comprehensive evaluations are conducted to stop infections from being transmitted through the donated organ. However, it is unfeasible to be entirely confident that the donor and their organ are entirely devoid of infection. Infections that may be passed from the donor encompass bacterial, viral, fungal, or other types of infections.
Other risks include cancer after kidney transplantation, although the probability is low, and serious infections such as HIV, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C, which remain rare.
There are currently efficient therapies for serious illnesses like HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Other viruses, such as human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8), can spread by transplantation.
What is the Kidney Transplant Success Rate in Iran?
Several factors affect the kidney transplant success rate in Iran. Patient age plays a role. Health issues like diabetes or high blood pressure matter too. Sticking to post-surgery medication counts a lot. The donated kidney’s quality also affects success.
In Iran, most new kidneys work well for at least ten years. After that time, 50 to 60 percent from living donors still function. Around 40 to 50 percent from deceased donors keep going.
You may want to learn more about “Kidney Donation Age Limit”.
Living donor kidneys succeed 99 percent of the time after one year. They reach nearly 94 percent at five years. Deceased donor kidneys hit 90 percent after one year. Their five-year rate sits between 75 and 80 percent.
Kidney Transplant Success Rates in Iran
Category | Living Donor | Deceased Donor |
1-Year Survival Rate | 99% | ~90% |
5-Year Survival Rate | ~94% | 75% – 80% |
10-Year Function Rate | 50% – 60% | 40% – 50% |
The table above shows that living donor kidneys survive longer and function better over time. Deceased donor transplants deliver solid results. They give many patients a key choice.
Kidney transplant programs in Iran combine comprehensive patient support with skilled medical care. Most patients have long-lasting success when they follow up, take their meds as prescribed, and get regular checkups. A transplant improves the quality of life.
How Much Does Kidney Transplant Surgery Cost in Iran?
Kidney transplant cost in iran is far less than most other countries. Low currency value and cheap living expenses drive down the price. One such surgery runs $12,000 to $15,000 on average. Low-cost kidney care pairs with top medical standards there. Patients gain quality treatment plus big savings.
Benefits of choosing Iran as a kidney transplant destination
There are a number of significant advantages to selecting Iran as a kidney transplant destination as the article highlights. All medically eligible patients can now start the transplant procedure thanks to Irans legally regulated system of incentivized living kidney donation which has virtually eliminated lengthy waiting lists.
In contrast to transplant destinations on the black market the Iranian model is subject to stringent government regulation and only qualified teams perform transplants at university hospitals guaranteeing greater medical safety and ethical standards.
The government pays for all transplant-related medical expenses greatly lessening the financial strain on recipients. In addition to protecting donors through legally binding agreements informed consent policies and assistance from authorized non-governmental organizations the system also prohibits donations to Iranian nationals in order to stop transplant tourism and exploitation.
In contrast to many other countries Iran has lessened the illicit organ trade decreased the risk of fraud and disease transmission and established a transplant system that is more open easily accessible and morally regulated.
Conclusion
Kidney transplant in Iran provides patients with kidney failure with a dependable affordable and cutting-edge medical solution. Kidney replacement surgery in Iran has gained credibility due to its well-defined legal framework skilled transplant teams and organized evaluation and follow-up procedures.
In contrast to many other countries, this option is particularly alluring due to favorable outcomes which are demonstrated by high kidney transplant success rate in Iran shorter recovery time from surgery and significantly lower kidney transplant costs.
Iran offers qualified patients pursuing kidney transplant surgery an easily accessible route to better quality of life and long-term health backed by open and honest processes thorough patient care and well-documented kidney transplant facts.
Which hospital in Iran is best for kidney transplant?
Tehran Kidney Hospital is highlighted as a leading center, where patients are closely monitored, and most spend a few days there post-transplant.
Is kidney transplant legal in Iran?
Yes, kidney transplantation in Iran is legal and strictly regulated by the government. Iranians cannot donate kidneys to non-Iranian recipients, but there is no requirement for a familial link between donor and recipient.
What is the success rate of kidney transplant in Iran?
The Kidney Transplant Success Rate in Iran is high: living donor kidneys have a 99% one-year survival rate and ~94% at five years, while deceased donor kidneys have ~90% one-year and 75–80% five-year survival rates.
What is the Expected Duration of Stay for Recipients and Donors During Kidney Transplant in Iran?
For monitoring including intensive care unit observation recipients usually remain in the hospital for a few days however the precise length of stay varies depending on each patients recovery.
Do kidney transplant patients need special care?
Yes, patients need close post-transplant care which includes renal transplant anti-rejection medications a post-transplant diet plan and routine kidney function monitoring. Understanding the signs of kidney rejection is crucial and long-term success is ensured by follow-up care.