
STD and infertility relation is a very important topic which is advised everyone to know about, whether they are women or men, want to have a baby or not. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) sometimes called sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can pass on from person to person by special bacteria, viruses, and parasites, through sexual or even nonsexual activities. Some specific STDs can directly or indirectly cause infertility in both men and women. It needs to be noted that some STDs may have no symptoms, so they remain undetected. These infections can develop, and proceed to the reproductive system which may damage reproductive organs or interrupt their normal function. Some STDs finally lead to infertility while others put pregnancies at risk. This article discusses how STDs transmit and which STDs can cause infertility in each gender. It also investigates how STDs can cause infertility in females and males. Keep reading to learn more about the role of STDs in men’s and women’s reproductive systems. Quick access What is STD? Who are at higher risk for contracting an STD? How are STDs Transmitted? Can STDs Cause Infertility? What STDs Cause Infertility? Can STDs Cause Infertility in Males? What STDs Can Make a Man Infertile? Can STDs Cause Infertility in Females? What STDs Can Make a Woman Infertile? How Long Does It Take for an STD to Cause Infertility? Infections That Cause Infertility in Females
STD stands for sexually transmitted disease. There are some specific bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause STDs, which can be transmitted from person to person through sexual or even nonsexual activities. Today more than 30 distinct STDs are known and the most common STDs are as follows: 1. Chlamydia 2. Gonorrhea 3. Syphilis 4. Human papillomavirus (HPV) 5. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) 6. HIV 7. Mycoplasma 8. Hepatitis B & C
Although everyone who has sexual activities is in danger of getting an STD, people who are in the below categories are at elevated risk of contracting an STD. • Having multiple sexual partners • Engaging in unprotected sex • Juvenile and young persons in their early twenties: Due to their increased unprotected sexual activities. • Sex workers • Gay men: Because of the nature of anal intercourse, that may lead to an increased chance of certain infections transmission such as gonorrhea, HIV, and syphilis. • Individuals with a history of STDs: They are at higher risk because of factors such as possible residual damage. • Having limited access to healthcare • Living where that has a higher STD prevalence • Drug and alcohol abusers: Using drugs and alcohol can lead to risky sexual behaviors.

There are specific STDs that can directly or indirectly cause fertility issues in both men and women. Since some STDs may have no symptoms; therefore, they go unnoticed. In these cases, infections may develop and advance to the reproductive system which causes damage, scarring, or inflammation. Some STDs finally lead to infertility while others endanger pregnancy. STDs are the most preventable cause of infertility which can be screened for and then treated. It is an easy and low-cost way in comparison to cure infertility later. It is advisable for sexually active persons and those who have concerns about STDs, to have safe sex, get regular tests, and consult with their health professional to learn about potential exposures and symptoms of STDs.
The fact is that not all STDs result in infertility. The chance of becoming infertile because of an STD depends on factors such as the duration and severity of the infection, the patient’s overall health, and the time when the STD is diagnosed and treated. Some STDs can cause infertility while others represent risk during pregnancy. Note: Having safe sex life and regular STI testing, remarkably prevent getting STDs and relevant infertility problems.
The most common STDs that may cause infertility:
|
STD |
Cause |
|
Chlamydia |
Bacterial infection |
|
Gonorrhea |
|
|
Syphilis |
|
|
Mycoplasma |
|
|
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) |
Viral infection |
|
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) |
|
|
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) |
|
|
Hepatitis B & C |
|
| Trichomoniasis |
Parasite Infection |

Several STDs impact fertility in men. It happens because These STDs can affect the male reproductive system, causing damage to the testicles, sperm, or the ducts that are responsible for carrying sperm. They can cause infertility or create fertility issues.
The most common STDs that can cause fertility problems in men include:
Chlamydia in men can reach the testicles and cause epididymitis, which is inflammation of the coiled tube called the epididymis located at the back of the testicles. Epididymitis can lead to scarring and blocking of the ductus deferens (vas deferens), which is the passageway that carries sperm from the testicles to the urethra. It results in reduced sperm quantity and mobility or even may make a man sterile.
Gonorrhea is also a bacterial infection that can spread to the man’s reproductive system, resulting in reduced sperm count and mobility or infertility due to blocked sperm ducts.
Syphilis can cause epididymitis in men. It results in reduced sperm quantity and mobility and affects their fertility. In the late stages of syphilis, it may cause gummas (soft, tumor-like growth of tissues) development. gummas may appear on the reproductive organs, causing damage, affecting their function, and leading to infertility.
HSV itself does not directly make men infertile. It can affect the quantity and quality of men’s sperm. Studies also show that containing Semen with HSV reduces sperm count, motility, and volume, and may affect its morphology and vitality. If sperm containing HPV fertilizes an egg, the risk of early miscarriage may be increased.
Generally, most HPV infections resolve spontaneously. HPV can only indirectly impact male fertility. HPV can decrease sperm count and motility, and alter its normal morphology, leading to decreased fertility or infertility in men. Therefore, fertilizing an egg with an infected semen with HPV may result in pregnancy loss.
Although Mycoplasma’s direct impact on male fertility is not as distinct as its impact on female fertility, untreated infections may cause epididymitis or/and urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) that may result in fertility issues in men. Studies show that Mycoplasma bacteria may also cause low motility of sperm cells by fastening themselves onto these cells. That can decrease men's fertility.
HIV directly doesn’t cause infertility. However, there are some specific factors related to HIV infection and its treatment that may lead to infertility.
Note: As HIV is an STD and can be transmitted sexually, it is safer to use assisted reproduction technology (ART) for having children based on your doctor’s suggestion. HIV-positive couples need to work closely with specialized healthcare providers. It optimizes the chances of a healthy pregnancy and childbirth.
Trichomoniasis usually doesn’t directly cause infertility. It can cause inflammation, burning, itching, and discharge in the genital area in men. Trichomoniasis may cause epididymitis, urethritis, and prostatitis (the inflammation of the prostate). These inflammations can cause disruptions in the function and movement of sperm. It can also reduce sperm motility.
Hepatitis B (HBV) & Hepatitis C (HBC) primarily target the liver; however chronic or severe HBV and HBC may impact fertility indirectly. HBV and HBC based on their severity degree can affect sperm morphology and cause lower sperm count and motility. Note: Hepatitis A (HAV) is not considered an STD, because it commonly spreads via consuming contaminated food or water.

Some STDs can result in female infertility if left untreated. These STDs can damage the genital organs, specifically the fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix, which can lead to infertility.
The most common STDs that can cause infertility in women include:
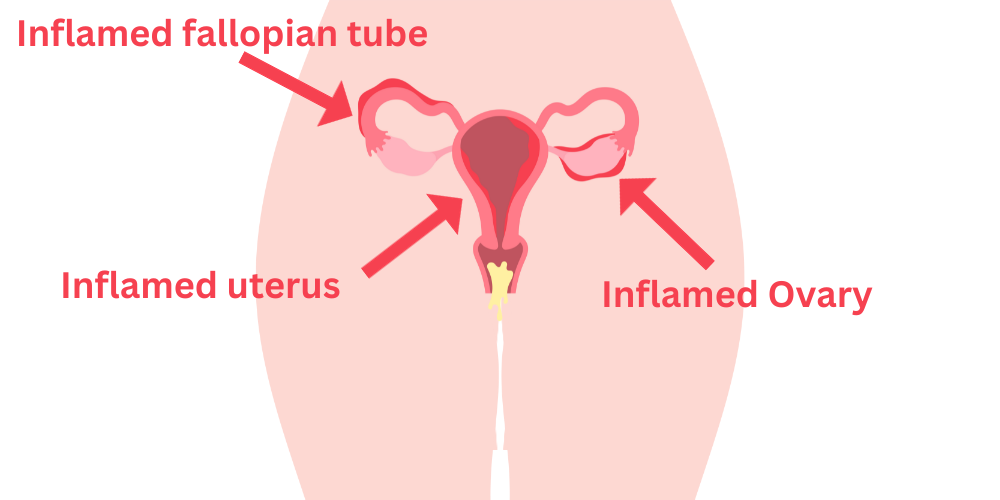
Chlamydia often has no symptoms, and if left untreated, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which is the infection and inflammation of women’s reproductive organs such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. Chlamydia can damage the mentioned organs permanently and lead to infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
 Gonorrhea
GonorrheaGonorrhea along with Chlamydia is one of the top two causes of PID that may lead to infertility and/or ectopic pregnancy if not treated.
Syphilis is a highly contagious disease that can lead to various issues. Syphilis can lead to PID, especially in its late stages. It damages women’s reproductive organs and finally can result in infertility. During Pregnancy syphilis can also pass from infected mothers to their unborn children during pregnancy or childbirth. This is a congenital syphilis that can cause various issues such as miscarriage, preterm birth, stillbirth, low birth weight, and other health problems in the baby. it can also impact the child's reproductive health in the future.
HPV infections mostly resolve automatically and they don’t influence fertility directly. There are different strains of HPV based on the degree of their symptoms.
HPV during pregnancy HPV influence on pregnancy and birth: HPV can increase the possibility of miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm birth, low birth weight, and other health problems for the baby, it also can potentially be transmitted to the baby during pregnancy, vaginal delivery, or breastfeeding. It may also affect the child's reproductive health in the future.
HSV effect on women’s infertility HSV-2 can impact female fertility only indirectly. The genital herpes caused by HSV may reduce women’s chance to get pregnant because intercourse is not recommended during an active herpes outbreak. HSV during pregnancy
As mentioned before HIV doesn’t directly cause fertility issues, but there are some factors related to HIV that may result in infertility.
Mycoplasma can infect the genitourinary tract, resulting in conditions like inflammation of the urethra and/or the cervix, and PID. PID may lead to scars and damage to the fallopian tubes. These scars can block the tubes, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg or for a fertilized egg to reach the uterus. It increases the risk of women’s infertility or ectopic pregnancy.
Generally, Trichomoniasis doesn’t directly cause infertility. It can cause itching, inflammation, burning, and discharge in the genital area in women. Sometimes, the infection can spread to the upper genital organs, causing PID and probable fertility issues in women. During pregnancy It may play an important role in preterm labor, and low birth weight in pregnancy.
These Chronic diseases can lead to chronic liver inflammation. Liver dysfunction affects hormonal balance in the patient’s body which plays a crucial role in women’s reproductive processes. They can also result in lousy nutrient absorption, which could affect women’s overall health for getting pregnant or during their pregnancy. Some HB medications may influence fertility ability. Note: Research has shown that women have a greater biological susceptibility to STDs than men, with a higher likelihood of transmission from men to women. This is because the female reproductive system is more vulnerable to infection than the male reproductive system.
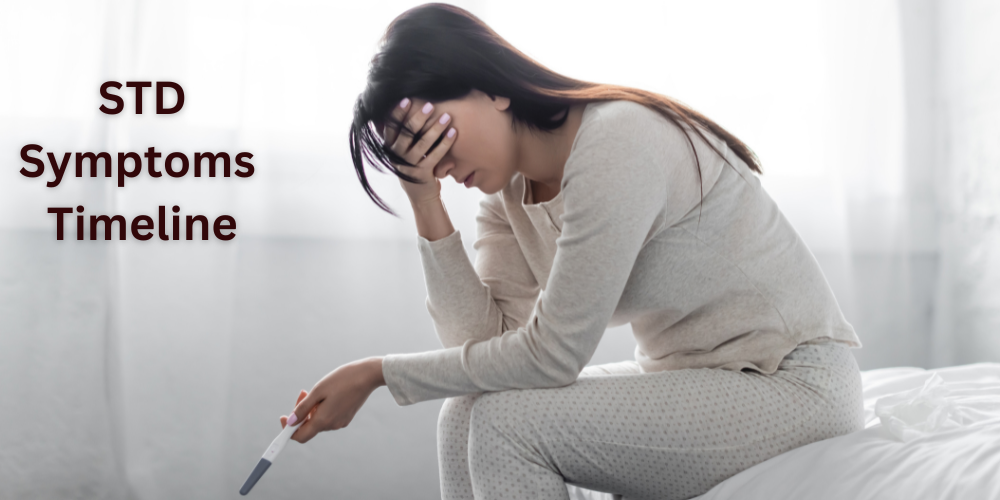
The time STDs take to cause infertility varies depending on several factors such as STD type (Some STDs can lead to infertility more quickly than others because of their aggressive nature), the severity of the STD, the presence of other infectious diseases, and the patient's immune system condition. The next section is a general overview of symptom timelines for some STDs.
 STD Symptoms Timeline
STD Symptoms TimelineGonorrhea If somebody gets symptoms, these usually develop between 1 and 14 days after exposure. Although most people who have chlamydia are asymptomatic. Chlamydia Symptoms may appear between 1 and 3 weeks after exposure. most people who have chlamydia don't show any symptoms. Hepatitis B Symptoms may be noticed 1-4 months after exposure, although many people might not show symptoms. HIV There are three phases for this STD: Acute phase: Symptoms may appear 2-4 weeks after infection with HIV. These symptoms resemble the symptoms of the Flu. This stage is called the acute phase Clinical latency: This phase is asymptomatic and can last a decade or longer without treatment. The virus is still active. AIDS: AIDS is the last phase of HIV in which the immune system is badly damaged. HPV The onset of symptoms can appear weeks, months, or even years after exposure. Trichomoniasis Some people get symptoms 5-28 days after exposure, while others are asymptomatic until much later. HSV The initial outbreak may happen 2 to 21 days after exposure. Recurrent or Subsequent outbreak is less severe than the initial outbreak, its duration is shorter, and may occur after weeks, months, or even years. Syphilis Primary stage symptoms can appear 10 days to 3 months after exposure. Secondary stage symptoms may be noticed 2 weeks to 6 months after the first symptoms. The latent (hidden) stage has no symptoms and can last for years. The tertiary stage is the most destructive stage. It can occur years after the initial stage.
STDs are the most common infection that can cause infertility or decrease fertility in women.
Except for STDs, other infections can also result in PID. Normal bacteria may get into reproductive organs when the natural barrier created by the cervix is damaged. It commonly happens in the following cases: 1- History of PID 2- There has been damage to the cervix because of
3- There have been procedures that involved opening the cervix
Another situation is when Harmless bacteria in the vagina can reach the reproductive organs. Although they are harmless in the vagina. They may cause infection in other organs. It may happen because of douching. Which is not advised by doctors. Note: Generally, Infections that cause PID may lead to infertility in women. Many types of bacteria can cause PID, but this disease is mostly caused by Chlamydia, gonorrhea, and some other STDs. An untreated PID damages the reproductive organs and may lead to tubal infertility.
Bacterial infection Sometimes tuberculosis can spread to other body organs such as the uterus and fallopian tubes and hurt them. This condition is called pelvic tuberculosis. It can cause PID and may lead to infertility.
It is the infection of the endometrium which is the lining of the uterus. Intense or long-standing endometritis may result in injury to the uterine lining. It makes implantation hard for a fertilized egg.
UTI is more common in women due to their shorter urinary tract in comparison to men. UTI can affect organs such as the bladder, uterus, and kidney. frequent UTI may lead to PID.
BV stands for Bacterial vaginosis. It happens when there are too many specific bacteria in the vagina. It alters the normal balance of the vagina, which may make it hard for the sperm to reach the uterus and therefore cause fertility issues. BV itself doesn’t directly cause infertility, however, untreated BV may cause several issues that may impact fertility. The issues are as follows: PID BV can increase the risk of developing PID known to cause tubal infertility in women. Contracting of other STDs BV can increase the risk of acquiring certain STDs such as chlamydia. Some of them can lead to PID, which, as mentioned, can impact fertility. Post-surgical infections Women with BV who undergo gynecologic surgeries such as abortion, dilation, and curettage are at a higher risk of developing a pelvic or uterine infection after the procedure, which may lead to fertility issues. During pregnancy Untreated BV increases the risk of premature birth or low birth weight. The timeline for these complications varies widely. PID can develop shortly after an STD or the spread of bacteria from BV, while infertility resulting from PID might not become apparent until a woman tries to conceive.
Yeast Infection usually doesn’t affect fertility directly. It may make intercourse uncomfortable due to soreness, itchiness, irritation, and swelling.
Fungal infection It is a common fungal infection that can cause vaginal infections. If it is not treated, can affect fertility. 
Click here for more information about iInfertility treatment in Iran

Comments & Questions