IVF failure is a frustration experienced by some IVF patients on their first attempt for a variety of reasons. IVF in is one of the most effective treatments for infertility. None of the clinics will guarantee a 100% IVF success rate for the procedure, even if you seek the best IVF clinic in your area. IVF failure reasons can vary widely from patient to patient.
Sometimes the IVF failure rate can be discouraging, especially for couples who enter the process with high hopes. When IVF failing occurs in early stages, it may feel devastating, yet understanding the common causes and solutions can help guide your next steps.
This article will help you identify the most common reasons for IVF failure reasons and what you can do if IVF keeps failing after IVF transfer.
What are the Reasons for IVF failure?
IVF failures are mostly caused by hormonal imbalances, low-quality eggs or sperm, uterine issues (thin lining, inflammation), lifestyle factors (smoking, obesity), issues with the embryo (chromosome abnormalities, poor quality), etc. These are among the most common IVF failure reasons reported by specialists.
We will consider some of the common reasons for IVF failure in the following:
Poor Embryo Quality
The poor quality of the embryo is one of the main reasons that IVF in Iran or anywhere else fails. Many embryos have defects that prevent them from implanting once they are transferred to the uterus, leading to failed IVF transfer outcomes.
Defects can lead embryos to die rather than grow, even if they appear healthy in the lab. In almost all situations, the reason you are unable to conceive is not a problem with your uterus. Because it is not healthy enough to grow, the embryo does not implant.
Would you like to learn about “hatching in IVF”?
Poor Ovarian Response
Occasionally, a woman’s ovaries may not react to fertility medications sufficiently. When this occurs, the likelihood of IVF success rate decreasing is higher. A woman may not generate enough eggs to produce a number of embryos for screening and possible implantation, particularly if she is older than 37 or has higher FSH levels.
When this occurs, the likelihood of IVF failing increases. After reviewing the situation, your reproductive endocrinologist could adjust your fertility drugs for the subsequent IVF cycle.
After reviewing the situation, your reproductive endocrinologist could adjust fertility drugs for the subsequent cycle in order to improve outcomes.
Uterine Issues
The most crucial organ for ensuring the fetus develops normally during the whole pregnancy is the uterus. The healthy growth of the fetus may be affected in women with uterine anomalies such as adhesions, fibroids, or poor lining. This can disrupt the IVF cycle timeline and may also be the primary cause of failed IVF rounds and failed IVF transfer, especially when IVF failing happens repeatedly.
Embryo Transfer Problems
One major reason IVF keeps failing is difficulties during the transfer itself. Optimizing embryo transfers by using advanced techniques and timing analysis such as ERA can significantly improve results and reduce the risk of failed IVF transfer.
Chromosome defects can cause even healthy-looking embryos to fail in the lab, and immune system dysfunction, infections, or inadequate blood flow can all lead to an unfavorable uterine environment.
Poor Sperm Quality
A healthy embryo can result from improved fertilization, which is facilitated by a healthy sperm. However, sperm quality and quantity may be poorer in guys with azoospermia, which can have a direct impact on the IVF treatment’s outcome.
As sperm quality declines the chances of producing an embryo with chromosome abnormalities increase. These embryos increase the likelihood of miscarriage in addition to increasing the likelihood of IVF success.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle plays a huge role. Women who want to begin IVF treatment must quit smoking and adopt an IVF diet rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamins for at least three months to improve outcomes. Compared to women who do not smoke, smokers require twice as many IVF rounds to conceive and have a significantly higher risk of miscarrying.
There is a lower chance of effective IVF treatment for women who are underweight or overweight. It all comes down to keeping a healthy weight. Even a small weight loss of 10 percent can have a significant impact on your chances of becoming pregnant if you are overweight.
Parental Genetic Abnormalities
One of the main causes of miscarriages is linked to genetic abnormalities. In addition to raising the possibility of IVF failure, patients with parental genetic diseases may give birth to a kid that has many problems.
Parental genetic issues can lead to repeated IVF effects like miscarriages or embryo abnormalities. Genetic testing is often recommended before another attempt.
Immune or Thrombophilia Issues
Immunological and thrombophilia issues that interfere with embryo implantation can lead to IVF failure. While thrombophilia, a bleeding disorder, can result in microthrombi that block blood supply to the uterus, certain immunological dysregulations may cause the body to unintentionally attack the embryo.
These conditions are associated with recurrent implantation failure, especially in certain circumstances like antiphospholipid syndrome, even if there is currently not enough evidence to recommend comprehensive screening for all thrombophilias and immunological variables in IVF patients.
Read more: IVF and autism
The abovementioned issues are common reasons couples extend their IVF journey with additional treatments such as blood thinners or immunotherapies. Blood thinners or immunosuppressants may be used in some circumstances under strict medical monitoring.
Endometriosis
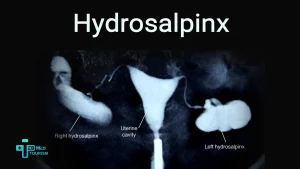
One prevalent cause of infertility is endometriosis. This can occur when endometrial tissue implants around the fallopian tubes or ovaries, where it may also result in scarring and inflammation.
A lower IVF success rate and IVF failing is kinked to advanced endometriosis. It frequently degrades the quality of eggs and may have an adverse effect on implantation.
A lower success rate with IVF and IVF failure is linked to advanced endometriosis. One important aspect in explaining this negative effect has been identified as surgical injury to the ovarian reserve after endometrioma removal.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS), which is mainly treated with preventative measures rather than directly causing IVF failure, can make IVF less successful by producing ovarian enlargement, fluid accumulation, and hormonal imbalances that impair implantation.
The main result of severe OHSS is that the current IVF cycle is essentially delayed or stopped by delaying the embryo transfer until hormone levels stabilize. OHSS can delay transfers, forcing a break between IVF cycles until hormone levels stabilize.
Unexplained Factors
Unknown causes of unexplained IVF failure occur when a successful egg retrieval, fertilization, and transfer of an apparently high-quality embryo do not result in implantation, leaving patients confused about IVF failure reasons.
Trial and error is a part of treatment. Multiple methods are tested. The most important thing here is patience. It’s also critical to maintain optimism.
With every try, additional details are revealed. Over time, understanding changes. Unknown causes of unexplained IVF failure occur when a successful egg retrieval, fertilization, and transfer of an apparently high-quality embryo do not result in implantation.
How To Cope With IVF Failure?
IVF failures affect not just your physical health but also your mental health. After an unsuccessful IVF attempt, you can be suffering through multiple phases of mourning until you find hope once more.
Acknowledge and Grieve
- After the first IVF failure its normal to accept sadness. After IVF allow yourself time to feel depressed sad and disappointed these are normal feelings. Take some time to grieve without passing judgment and concentrate on your mental well-being.
- Spend some time focusing on your mental health and grieving without passing judgment.
- Write in your journal, cry, or talk to a trusted person to express your feelings.
Build a Support System
- Surround yourself with supportive family, friends, or support groups who understand the pain of IVF fail. Use open communication and mutual support to rely on your relationship.
Make contact with friends and relatives who can offer sympathy and understanding. - To exchange stories with people who have gone through similar struggles, join a support group.
Seek Professional Guidance
- To manage anxiety and depression, speak with a mental health specialist who specializes in infertility.
- Review the unsuccessful cycle, look into the reasons, and talk about your options for the future with your infertility specialist.
Practice Self-Care
- Take part in relaxing activities and pursuits that make you feel happy and at ease.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle by getting enough sleep, exercising, and eating a balanced diet. - Treat yourself with kindness and stay away from needless triggers, like offensive material on social media.
Plan for the Future
- Take some time to feel better physically and emotionally before making any new decisions.
- Discuss potential reasons for the failure with your doctor and consider other options like PGT-A or modified protocols and choose the best IVF protocol.
- Rekindle your passions and remind yourself that your identity is not entirely defined by your role as a parent.
Is There Treatment for Recurrent IVF Failure?
Yes the underlying causes of recurrent IVF failure also referred to as recurrent implantation failure (RIF) such as immunological factors blood coagulation issues and anatomic abnormalities can be addressed. Let’s consider the above and some other treatments for recurrent IVF failure in the following:
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT-A/PGS)
Before transferring embryos, the IVF add-on known as Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A), formerly known as PGS, checks them for aneuploidy, or an abnormal number of chromosomes.
To increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy and lower the danger of miscarriage, a biopsy of a small number of the embryo’s cells is extracted, and the cells are then examined to identify euploid (normal) embryos for transfer.
Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA)
In order to identify a woman’s unique “window of implantation” (WOI) for embryo transfer—the time when her endometrium is most receptive to an embryo—the Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA), a customized embryo transfer test in IVF, examines a uterine lining biopsy.
Doctors can more accurately time the progesterone and embryo transfer by using the ERA test to classify the endometrium as receptive, pre-receptive, or post-receptive based on gene expression patterns. Patients who have experienced repeated implantation failure following prior IVF cycles with high-quality embryos are frequently given this option.
Hysteroscopy
During a hysteroscopy a minor surgical procedure done before IVF doctors can see and assess the inside of the uterus directly. This allows them to identify and possibly treat conditions like fibroids polyps and scar tissue that could prevent embryo implantation and a positive pregnancy.
Particularly for patients with a history of failed IVF cycles it is a helpful diagnostic and therapeutic tool that aids in creating the ideal uterine environment for embryo transfer. It is not always standard advice for all patients though.
Adjusted Stimulation Protocols
In IVF treatment, adjusted stimulation protocols tailor ovarian stimulation by changing drug types (agonist, antagonist, or milder regimens), dosages, and timing to a patient’s ovarian reserve, past IVF results, age, and body mass index.
Egg quality and quantity are to be maximized while risks such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) are minimized. Modifying gonadotropin dosages with oral medications like letrozole or switching from long agonist protocols to shorter antagonist or minimum stimulation regimens are common changes made to improve patient satisfaction and efficacy.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
A specific type of IVF called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) uses a micropipette to inject a single sperm directly into an egg rather than depending on the sperm fertilizing the egg on its own.
In order to enable couples to have a genetically related kid, this approach is mostly utilized to overcome male infertility, such as very low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or aberrant sperm shape.
Similar to a typical IVF cycle, the resultant embryo is grown in the laboratory after fertilization before being placed in the uterus.
Treatment for Endometriosis
Some experts believe that surgical removal of the endometriosis is necessary even if IVF is required. The apparent justification for this is that the cysts will disrupt the IVF treatment cycle and lower the likelihood of IVF pregnancies.
Despite its apparent logic, this is incredibly illogical. Since endometriosis is external to the uterus and will not impact the embryos that implant there, there is no need to treat endometriosis directly if you have it and require IVF.
As a matter of fact, your chances of having a successful IVF procedure can be decreased by needless laparoscopic surgery. The ovarian reserve is further decreased when the chocolate cyst is removed because it damages the healthy ovarian tissue nearby.
Endometriosis patients already have a diminished ovarian reserve, and surgery just makes it worse. As a result, they are unable to produce high-quality eggs after undergoing IVF procedures.
Immunological Treatments
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), steroids, and intralipid infusions are examples of immunological treatments for IVF that are intended to modify the immune system’s reaction during IVF, especially for patients who have recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) or repeated implantation failure (RIF).
As advised by the Human Fertilization and Embryology Authority (HFEA), these treatments should only be considered in certain circumstances and under close medical supervision because their efficacy is debatable, and some evidence points to serious potential harm without demonstrated benefit.
Donor Eggs or Sperm
IVF uses donor eggs or sperm when an individual or couple is unable to use their own genetic material because of infertility, genetic concerns, or personal preference. For elderly patients or those with poor egg quality, donor eggs from a young, viable donor greatly increase the likelihood of high-quality embryos and overall success rates.
When a male partner is unable to produce viable sperm, donor sperm is utilized by single women or same-sex couples in need of a sperm supplier. Double donation is the practice of creating embryos for transfer using both donor sperm and donor eggs.
Surrogacy
The majority of gestational surrogate pregnancies are obtained using in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF is the process of creating an embryo in a lab using either an egg and sperm donor or the intending parents’ egg and sperm. After that, the embryo is placed inside the carrier’s uterus.
Lifestyle Optimization
Maintaining a healthy weight getting regular moderate exercise getting enough sleep practicing stress management avoiding harmful substances like tobacco excessive alcohol and caffeine and eating a balanced whole-foods diet high in antioxidants vitamins and healthy fats are all part of optimizing ones lifestyle for IVF.
By enhancing overall well-being regulating hormones improving egg and sperm quality and creating a supportive environment these changes maximize the success of IVF treatments.
Supplements and Adjunct Therapies
Although supplemental therapy and supplements are becoming more and more popular there is conflicting evidence regarding their effectiveness in IVF. CoQ10 melatonin and DHEA are among the supplements that may improve ovarian response and egg quality especially in certain patient groups.
Myo-inositol may benefit women with PCOS while vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids may enhance specific IVF outcomes. Some treatments like heparin and low-dose aspirin have inconsistent effects and others like growth hormone and testosterone are commonly used rashly without enough evidence. A simple and effective dietary approach is to follow a Mediterranean diet.
Personalized IVF Protocols
Customized IVF techniques adapt the process to each patients unique characteristics such as age ovarian reserve and hormone levels in order to improve success rates and lower risks.
These customized regimens may include preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) and specialized embryo transfer procedures as well as adjustments to the types and dosages of fertility medications and routine blood tests and ultrasounds to monitor ovarian response. Every patient should have a more successful stress-free and efficient fertility journey.
Positive aspects of IVF Failure
Even though a failed IVF cycle is a terrible experience, there are some possible benefits, such as learning more about the reasons behind infertility, having the chance to adopt healthier lifestyle choices, having the chance to explore other family-building options like adoption or using donor gametes, and having the chance to learn new coping skills with supportive counseling.
A failed cycle may also serve as a springboard for some people to consider other family structures or to concentrate on objectives other than starting a family.
How Long After Failed Implantation Will a Period Start?
After an unsuccessful implantation your period usually begins one to two weeks later or by the time you stop taking your progesterone support medication. With IVF your period might arrive on time or a bit later.
The precise date can be affected by variables like the individual’s hormone levels and the type of IVF treatment. It is advised that you seek individualized guidance from your fertility specialist if your period doesnt come as planned or if you have any concerns.
Conclusion
The IVF failure is emotionally draining regardless of whether this is the 1st IVF failure or whether IVF failing continues in subsequent cycles. Couples may be frightened by the IVF failure rate, yet each failed effort also provides insight into possible symptoms and remedies for IVF failure, including understanding repeated failed IVF transfer events.
IVF effects can be physically, emotionally, and financially demanding. Yet, with persistence, modern science, and medical support, each attempt brings patients closer to success.
It’s common to experience disappointment or even depression following an unsuccessful IVF attempt, but there are still choices accessible with the correct medical and mental support.
At TebMedTourism, we believe every failed attempt is not the end of the journey but a step toward new hope. If you reach out to our expert team, they will provide you with international patient support and affordable treatment plans to help you explore all possibilities—from IVF and genetic testing to surrogacy—while receiving continuous guidance at every stage.
What happens to your body after failed IVF?
Hormonal medications stop after IVF fails, resulting in a withdrawal bleed (your period) within 1-2 weeks. Following a failed IVF attempt, you can also experience physical exhaustion, bloating, or psychological distress like feeling helpless.
Why does IVF fail with good embryos?
Even high-quality embryos may not implant due to hidden genetic issues, uterine problems, immune responses, or timing mismatches. This is one reason the IVF failure rate exists despite good embryos.
Why does IVF fail the first time?
Poor embryo quality, problems with the uterine lining, or lifestyle choices are frequently the causes of the first IVF failure. A lot of couples have to make multiple attempts before they are successful.
What to do after failed IVF?
If IVF keeps failing, talk to your doctor about the cycle, think about PGT-A or ERA testing, improve your lifestyle with an IVF diet, and take some time to heal emotionally.
When should you expect your period after failed IVF?
Most patients get their period within 1–2 weeks after implantation failure or when progesterone support stops. Delays can occur depending on hormones, but if your period doesn’t arrive, contact your fertility specialist.
Why do embryo transfers fail?
Poor embryo quality chromosome abnormalities fibroids or thin lining in the uterus immune or blood-clotting disorders incorrect implantation timing or technical difficulties during the transfer itself can all cause embryo transfers to fail.
Why can IVF fail?
Hormonal imbalances poor quality eggs or sperm embryo defects uterine abnormalities lifestyle factors (like smoking or obesity) genetic problems endometriosis or undetected factors despite normal test results are some of the reasons why IVF can fail.
What should you do after 3 failed IVF cycles?
After three failed IVF cycles, it is recommended to review all previous cycles with a fertility specialist, investigate underlying causes, and consider advanced options such as PGT-A, ERA testing, hysteroscopy, adjusted stimulation protocols, or donor eggs or sperm if appropriate.
How long after a failed IVF can you do the next one?
Most patients can attempt another IVF cycle after one to two menstrual cycles, once hormone levels stabilize and both physical and emotional recovery are adequate, though timing should be personalized by the fertility specialist.