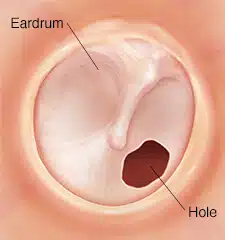
Tympanoplasty also considered as an eardrum repair is a special surgery to recreate and reconnect the tiny bones of the inside of the ear to eardrum. Punching the tympanic membrane is our topic and we are going to provide different information about this surgery and its purpose. Keep on. There are two fundamental reasons for Eardrum perforation:
- Chronic infection of ears
- Trauma in ear
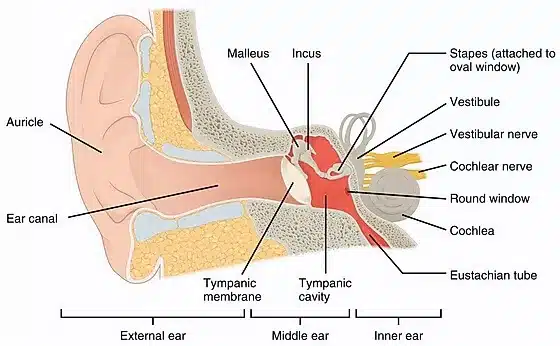
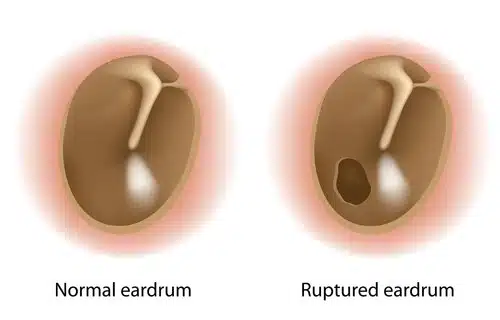
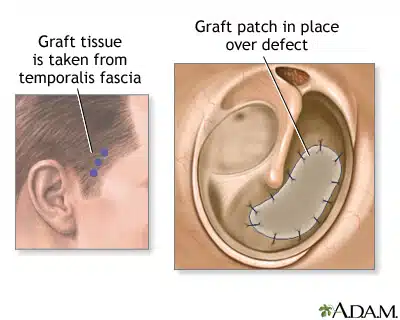
Diagnosis/Preparation of tympanoplasty
- A microscopic exam
- an audiogram of the hearing loss
- A history of the hearing loss
- Vertigo or facial weakness test
- blood and urine studies
In some cases a fistula test can be considered if the patient is suffering from a marginal perforation of the eardrum. Different types of tympanoplasty need different preparation methods for surgery. A hearing test can identify any hearing deficiency. You do not sense any hurt during the procedure because a tympanoplasty is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia.
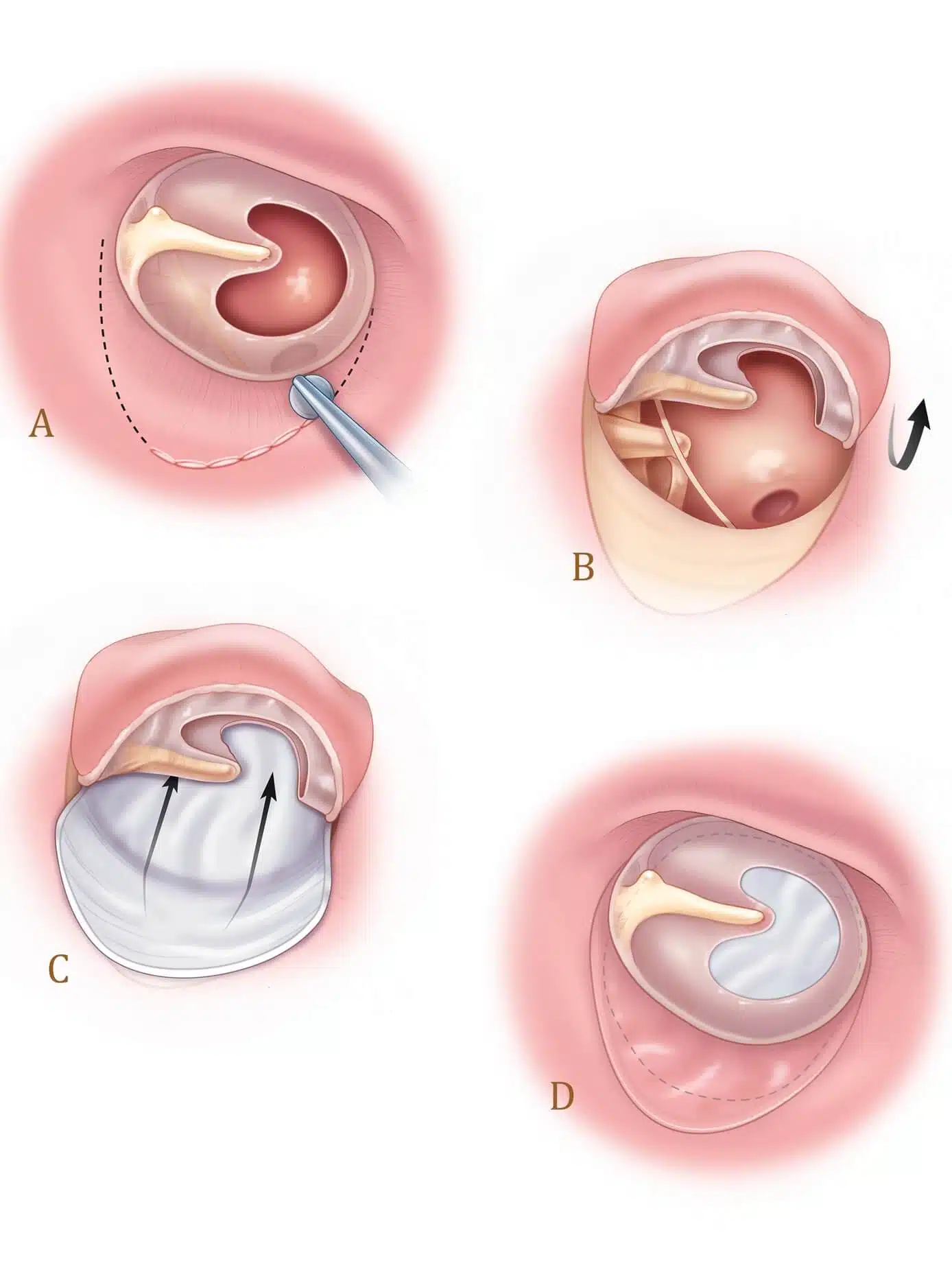
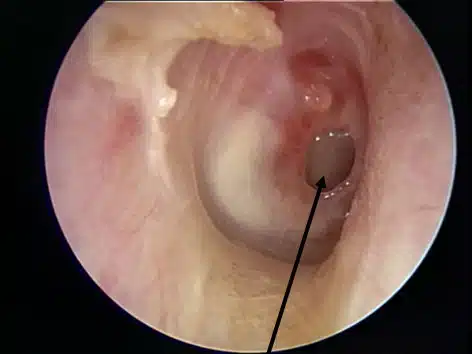
Before and after of tympanoplasty surgery
In 2 to 3 hours after surgery, you can return to your home. You need to take some antibiotics. Make sure to keep water away from your ear. If there are allergies or a cold, ask your surgeon to prescribe antibiotics and a decongestant. The packing is removed under the operating microscope after 10 days and during these days you also need a mild pain reliever. Possible tympanplasty surgery risks include failure of the graft to heal causing recurrent eardrum perforation; narrowing (stenosis) of the ear canal; scarring or adhesions in the middle ear; perilymph fistula and hearing loss; erosion or extrusion of the prosthesis; dislocation of the prosthesis; and facial nerve injury.