Dacryocystorhinostomy is a surgery that aims to reduce fluid and mucus retention inside the lacrimal sac. It increases tear drainage to relieve epiphora. Dacryocystorhinostomy surgery can be done in an endonasal or external approach. Both approaches allow tears to directly drain from the canaliculi into the nasal cavity via a new low-resistance pathway.
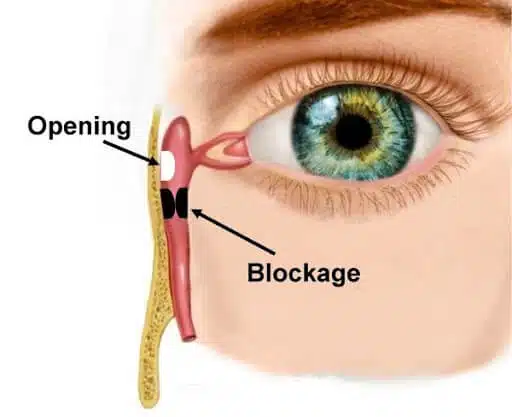
Dacryocystorhinostomy overview
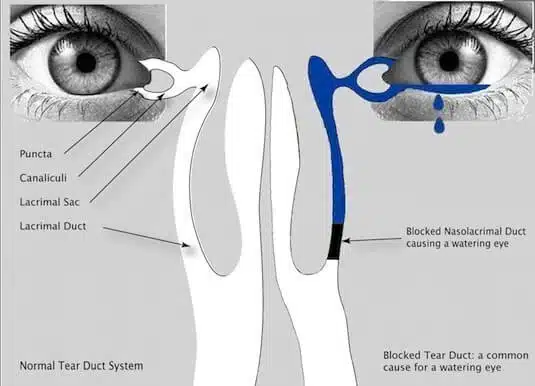
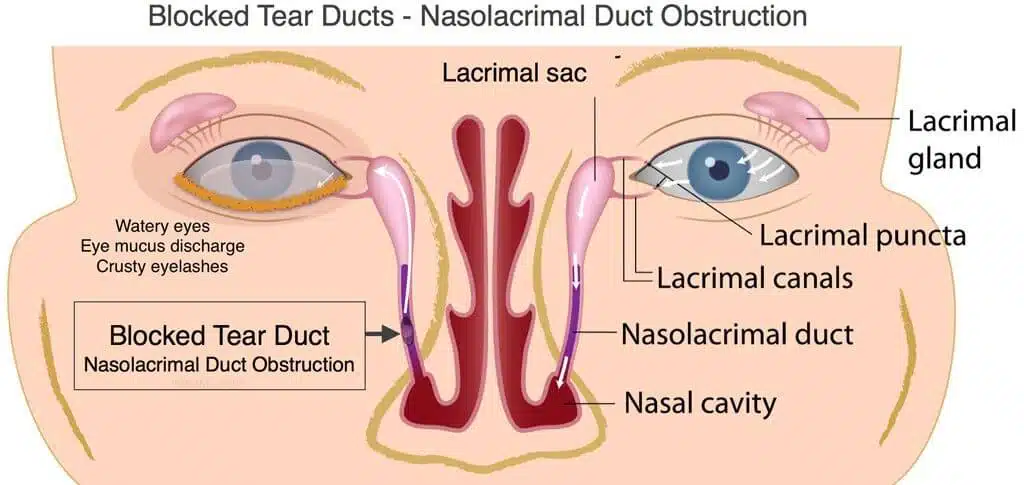
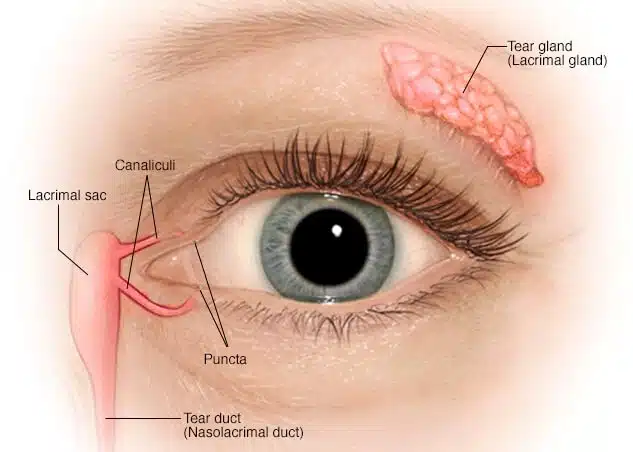
A dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a type of surgery that makes a new hole to enable the lacrimal sac to drain freely into the nose. This surgery is done when the tear duct, which is responsible for draining the lacrimal sac, gets blocked and prevents the drainage of tears away from the lacrimal sac. A patient that suffers from a blocked tear duct often has epiphora (excess tearing) or recurrent eye infection. It means that the tears spill out because they cannot drain from the eyes into the back of the nose. The patient may also experience inflamed and enlarged lacrimal sacs and infections and inflammation around the eyes.
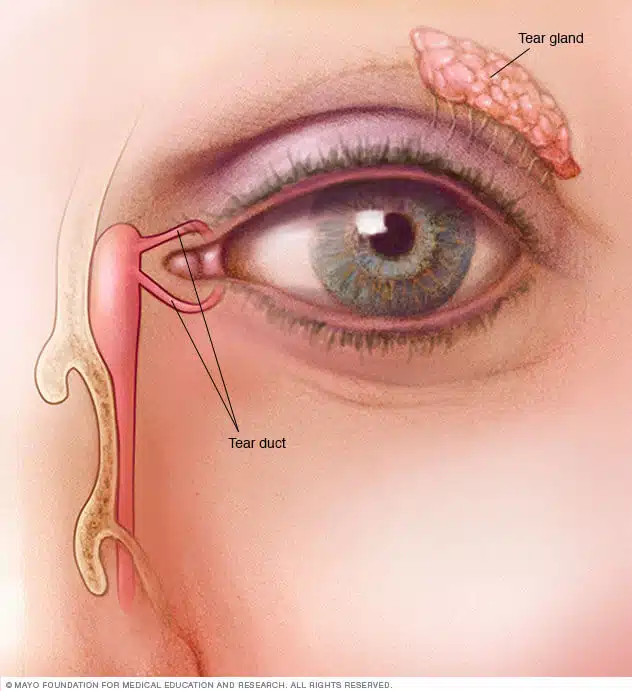
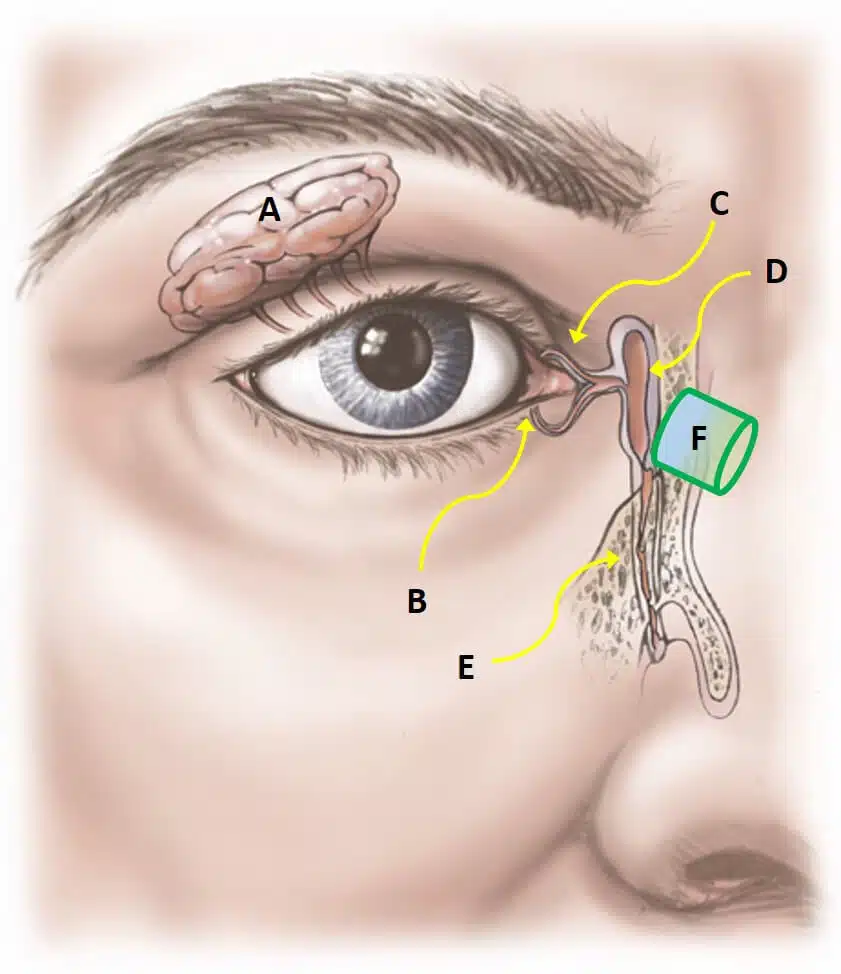
Causes of a blocked tear duct
Blocked ducts can occur at any age. The causes include:
- Congenital blockage: Many infants are born with this condition because their tear drainage system is not fully developed.
- Age-related changes: As individuals age the tiny openings that drain tears may get slender or the nose can barricade the tear ducts.
- Injury or trauma Damage to the face can lead to bone injury or scarring near the drainage system and interpret the regular tear flow through the ducts. Even, slack skin cells or small particles of dirt camped in the duct can cause a blockage.
- Infection or inflammation: MChronic infection or inflammation of your eyes or nose may cause the blockage of tear ducts and make the dacryocystorhinostomy necessary.
- Inflammatory conditions: Disorders that lead to swelling such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis or sarcoidosis can increase the risk of tear duct blockage.
- Cancer treatments: Chemotherapy medication and radiation treatment are done for cancer and can lead to a blocked tear duct.
How is dacryocystorhinostomy done?
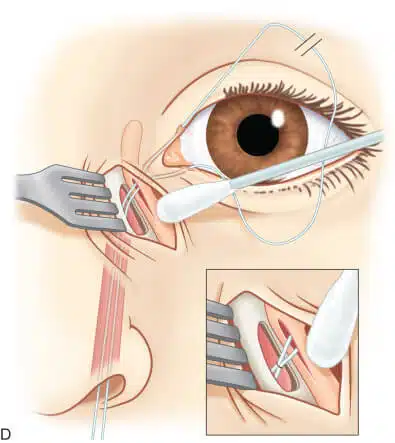
External dacryocystorhinostomy may be done under general anesthesia or monitored sedation. The surgeon makes a curvilinear incision at the level of medial canthal tendon and extends it into the thin skin of the lower lid. The incision is approximately 10 to 12 mm. your face is already prepped and draped in the sterile fashion. Surgeons often place a lubricated protective lens on the ocular surface to preserve the globe during the surgery. The surgeon incises your skin with a 15-blade scalpel or monopolar unit. Then he/she holds the orbicularis muscle fibers apart until the periosteum of the anterior lacrimal crest is detected. To avoid bleeding, the cut should be lateral to the angular vessels.